Geography Reference
In-Depth Information
Determining Where Something Is: Coordinate Systems
Cartesian Coordinate Systems
A coordinate system is a way of determining where points lie in space. We are interested in two-
dimensional (2-D) space and three-dimensional (3-D) space. In general, it takes two numbers to assign a
position to a 2-D space and three numbers in 3-D space.
Coordinates may be thought of as providing an index to the locations of points in space, and hence to the
features that these points define.
To make a 2-D Cartesian
5
coordinate system, draw two axes (lines) that cross at right angles on a piece of
paper. The point at which they cross is called the “origin.” The sheet of paper is the x-y plane. Arrange
the page on a horizontal table in front of you so that one line points left-right and the other toward
and away from you. The part of the line from the origin to your right is called the positive x-axis. The
line from the origin away from you is called the positive y-axis. Mark each axis in equal linear units
(centimeters, say) starting at the origin, as shown in Figure 1-5. Now, a pair of numbers serves as a
reference to any point on the plane. The position x = 5 and y = 3 [shorthand: (5,3)] is shown.
You can create a 3-D Cartesian coordinate system from the 2-D version: Imagine a vertical line passing
through the origin; call it the z-axis; the positive direction is up. Now you can reference any point in three-
dimensional space. The point x = 5, y = 3, and z = 4 [written more concisely as (5, 3, 4)] is shown in Figure 1-6.
This is called a right-hand coordinate system. The thumb, forefinger, and middle finger represent the
positive axes x, y, and z, respectively. With your right hand outstretched, arrange those three digits so
that they are roughly mutually orthogonal—that is, with 90
o
angles between each pair. Point your thumb
to the right and your forefinger away from you. Now your middle finger will be pointing up.
6
5
4
3
(5,3)
2
1
1234
1
56
x
FIGURE 1-5 2-D Cartesian coordinate system
5
Descartes, who lived from 1596 to 1650, made major contributions to both mathematics and philosophy. Descartes is
credited with integrating algebra and geometry, by inventing the coordinate system that (almost) bears his name.
6
It's best not to practice this exercise where other people can see you.


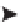



















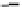





Search WWH ::

Custom Search