Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
y
A
0
V
0
y
A
2
y
A
1
V
2
V
1
M
2
M
1
O
1
O
0
O
2
x
A
2
x
A
1
x
A
0
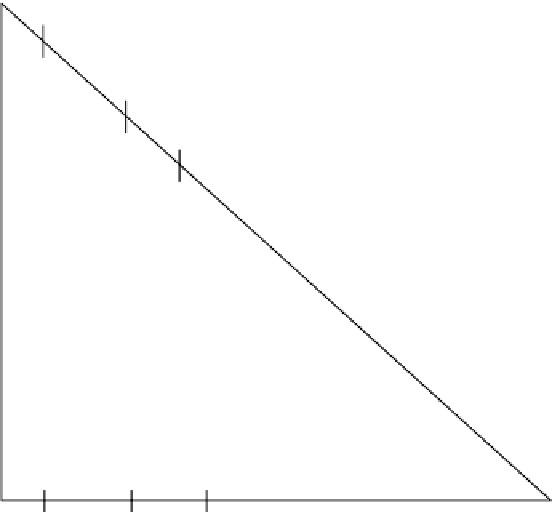
Figure 5.7
Triangular diagram depicting cross-flow cascade.
Example 5.1: cross-flow cascade
Problem:
Acetic acid (vinegar) is a common component in the waste stream of various
fermentation processes. This process represents a significant environmental concern
because the manufacture of pharmaceuticals can result in carboxylic acid-containing
by-products. The carboxylic acid byproducts must be removed from the pharmaceuti-
cal products as well as any water streams prior to discharge. Isopropyl ether has been
used as a solvent for extraction. The isopropyl ether is then distilled and recycled
back to the extraction process. As an example, a feed that is 30 wt% acetic acid and
70 wt% water is fed to a two-stage cross-flow cascade. Feed flowrate is 1000 kg
/
hr,
hr of solvent containing 99 wt% isopropyl ether and 1% acetic acid is
added to each stage. Operation is at 20
◦
C and 1 atm where the equilibrium data are
given in Table 5.1 [2]. Determine:
(a) the weight fractions of the outlet raffinate and the two outlet extract streams;
(b) the flowrate of the outlet raffinate.
Solution:
Figure 5.8 is a schematic of the example. Point
O
0
and point
V
0
are plotted on Figure 5.9,
with a line connecting them. The
x
-coordinate of the first mixing point,
M
1
,was found
from the equation:
and 1250 kg
/


Search WWH ::

Custom Search