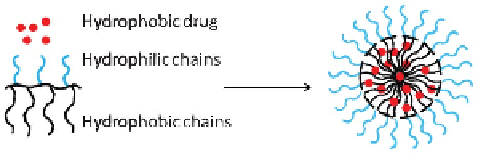
Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
cells.
48
Recently, Cheng et al. employed a fluorescence-resonance energy-transfer
(FRET) technique to demonstrate that PEG-b-PDLLA micelles were not stable in
the bloodstream due to the influence of a-andb-globulins rather than c-globulin
or serum albumin.
49
Based on those results, Cheng et al. summarized the possible
mechanisms responsible for the micelle decomposition induced by serum
proteins,
41
including protein adsorption,
48,49
protein penetration,
50,51
and drug
extraction.
41
What exactly happens to the micelles after injection is poorly
understood because it is hard to measure and estimate micelle concentration
locally in the bloodstream.
52
Cheng et al. tracked unmodified copolymer micelles
using the FRET imaging method, but unfortunately no direct evidence proved
that the CMC was unchanged by incorporating a FRET pair.
53
However, there is no doubt that, directionally, the lower the CMC, the higher
the probability of micelle stability in the bloodstream. Therefore, the most
common strategy to enhance the micelle stability is to reduce its CMC. Compared
to liposomes, polymeric micelles usually have a much lower CMC, at a micromolar
level, which imparts a higher stability. A further reduction of polymeric micelle
CMC can be achieved by increasing the core-forming block hydrophobicity,
molecular weight, or both.
40
One example is that of chemically modified Pluronics:
Pluronic/PCL copolymeric nanospheres exhibited a lower CMC.
54,55
Another
interesting finding is that stearic acid as side chains can keep micelles stable even in
thepresenceofserum.
56
In the presence of serum albumin, a-andb-globulins, or c
globulins, the micelles from PEG-b-poly(N-hexyl stearate
L
-aspartamide) (PEG-b-
PHSA) copolymers with nine stearic acid side chains still existed after two hours.
Crosslinking is a straightforward method to stabilize micelles. While the
covalent crosslinking of the micelle core or shell can inhibit burst release from a
stable micelle, it can also inhibit or prevent micelle dissociation. For instance,
PEG-PCL micelles with cores crosslinked by radical polymerization of the
double bonds introduced to the PCL blocks turned out to be more stable.
57
Biodegradable thermosensitive micelles with crosslinked cores formed from
PEG-b-[N-(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylamide)-oligolactates] [PEG-b-p(HEMAm-
Lac
n
)] kept their integrity upon dilution and only degraded after cleavage of the
ester bonds in the crosslinkers.
58
The caveat, however, is that crosslinking reactions usually occur after core
formation, which can alter the structure and properties of the encapsulated
drug. To overcome this potential problem, our group developed stable core-
surface
d
n
4
y
3
n
g
|
2
crosslinked
micelles
(SCNs),
shown
in
Figure 3.6,
made
from
Figure 3.6
Formation of SCNs from amphiphilic brush polymers. Adapted with
permission from ref. 59. Copyright 2004 American Chemical Society.