Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
d
n
4
y
3
n
g
|
7
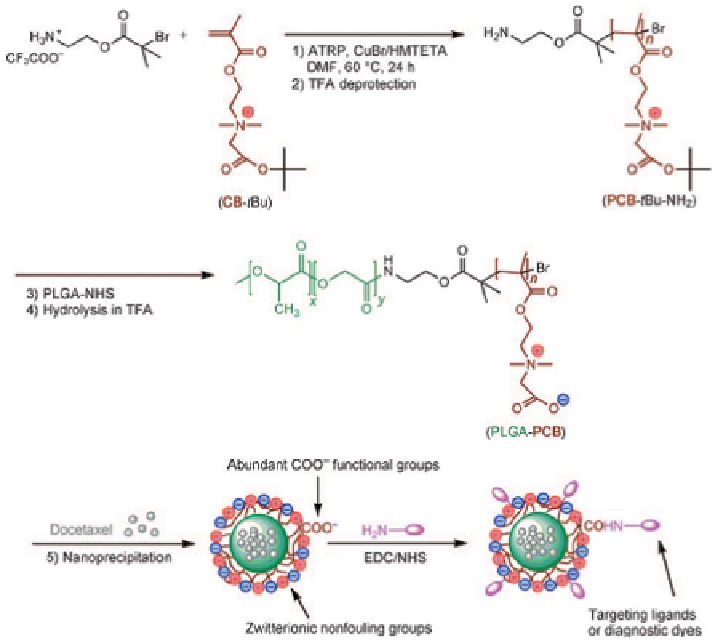
Figure 10.5
Synthesis of PLGA-PCB copolymers, formation of PLGA-PCB/Dtxl
NPs,
and
post-functionalization
of
NPs
with
targeting
ligands
or
diagnostic
dyes.
DMF 5 N,N-dimethylformamide;
HMTETA 5
1,1,4,7,10,10-hexamethyltriethylenetetramine;
TFA 5 trifluoroacetic
acid. (Reproduced from Cao et al.
18
with permission from Wiley.)
unchanged for over 6 months. The nanogels show low macrophage uptake and
significant cellular uptake by human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC)
after being conjugated with a targeting ligand, cyclo[Arg-Gly-Asp-
D
-Tyr-Lys],
implying potential low interaction with the innate immune system and high
specific selectivity to targeted cells. The disulfide bonds in the nanogel can
facilitate the degradation and accelerate the spontaneous release of the
encapsulated model drug and Fe
3
O
4
nanoparticles upon exposure to the
reducing environment.
Both experiments indicated that nano drug carriers protected by the CB-
based ''nonfouling'' materials could realize compatibility at both the protein
level and cellular level. Also the results demonstrated the advantage of the CB
''nonfouling'' materials in functionalization without compromising the
resistance to nonspecific protein adsorption. These results imply that these
two systems could potentially be used for in vivo drug delivery.