Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
d
n
4
y
3
n
g
|
0
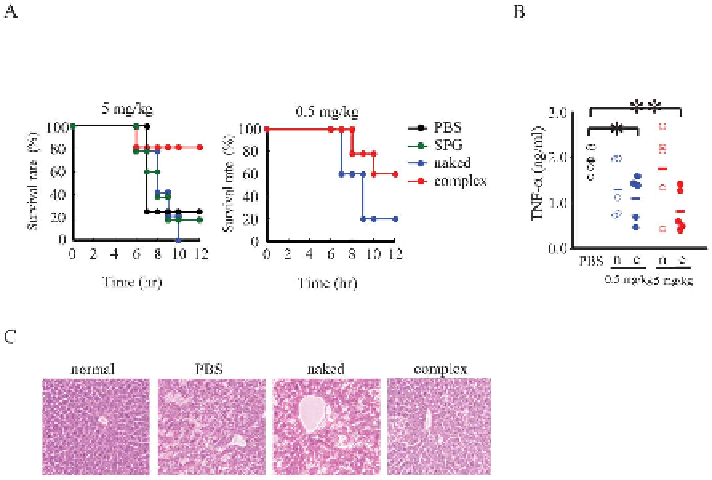
Figure 8.7
AS-ODN/SPG-mediated TNF-a inhibition on the progression of LPS/D-
GalN-induced fulminant hepatitis. (A) Survival rate of the mice treated
i.p. with PBS, SPG, AS-ODN, or AS-ODN/SPG before hepatitis
induction. The animals were protected with the preceding treatment; at
24 h later they were i.p. co-injected with LPS/D-GalN and SPG, AS-
ODN, or AS-ODN/SPG, and the survival rate to 12 h was obtained (n 5
5). (B) TNF-a level in the serum was measured at 1 h after LPS/D-GalN
administration. The blood was obtained by retro-orbital bleeding (n 5 5).
n and c represent naked AS-ODN and complexed AS-ODN/SPG
administration, respectively; *P , 0.05, **P , 0.01. (C) A representative
liver histology of LPS/D-GalN-induced hepatitis in mice injected with
PBS, AS-ODN, or AS-ODN/SPG (5 mg kg
21
). At 6 h after LPS/D-GalN
injection the livers were stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E).
Original magnification 6200.
now known to be more abundantly expressed by macrophages themselves,
although it was first reported as a T lymphokine acting on macrophages. MIF
is constitutively expressed in macrophages, with MIF protein preformed in
cytoplasmic stores.
63
The experimental approach to antagonize MIF actions
was usage of neutralizing anti-MIF antibodies. This has proven therapeutically
effective in several models of autoimmune disease, such as IBD,
64
experimental
autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE),
65
and arthritis.
66
Antibody-based anti-
MIF drugs have significant associated risks and limitations, including their
potential immunogenicity, their short half-life in vivo, possible side effects, and
the high cost of their application. Therefore, if there is a nucleotide base
therapy such as antisense DNA and siRNA available, it would be a great
advantage.