Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
a
hydrophilic
stabilizing
block
were
demonstrated
to
target
cancer
cells
overexpressing CD44 glycoprotein receptors.
53
6.5 Tumor-Targeting Polymersomes
Targeting polymersomes were developed to enhance the drug outcome of the
polymersome formulations by decorating the polymersome surface with
targeting ligands like antibodies, RGD, and folic acid. For instance, Jiang
and co-workers reported that lactoferrin-conjugated polymersomes with
loaded tetrandrine and DOX could pass the blood-brain barrier (BBB),
accumulate at the tumor site, and shrink the tumor in glioma-bearing rats.
54
Kokkoli and co-workers reported that PR_b-functionalized PEO-PBD
polymersomes (PR_b is an effective a5b1 targeting peptide) efficiently
delivered tumor necrosis factor-a (TNFa) to LNCaP human prostate cancer
cells, resulting in a dramatic enhancement of the cytotoxic potential of
TNFa.
55
The targeting effect significantly outperforms GRGDSP-functiona-
lized polymersomes in terms of promoting cell binding/internalization and
DOX cytotoxicity.
56
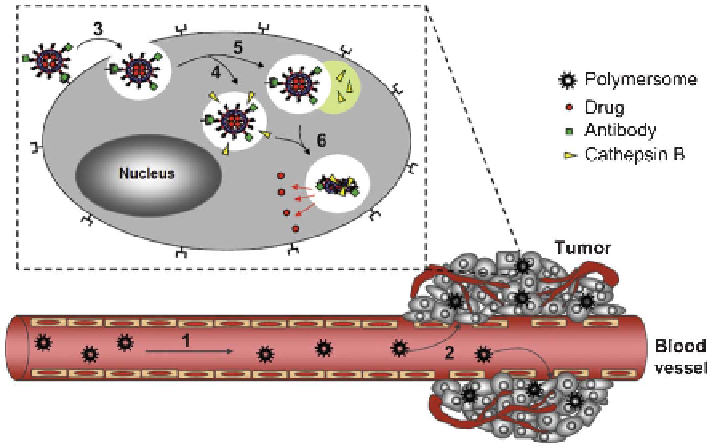
Feijen and co-workers have developed anti-EGFR
modified polymersomes based on a PEG-pep-PDLLA copolymer containing
a
d
n
4
y
3
n
g
|
4
lysosomal
enzyme
cathepsin
B
cleavable
peptide
for
systemic
cancer
(Figure 6.8).
57
chemotherapy
Recently,
Lecommandoux
and
co-workers
Figure 6.8
Schematic illustration of systemic targeting drug delivery by using
antibody conjugated and peptide-containing PEG-pep-PDLLA poly-
mersomes
in
which
therapeutic
drugs
or
proteins
are
present.
(Reproduced from Lee et al.
57
with permission from Elsevier.)