Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
d
n
4
y
3
n
g
|
3
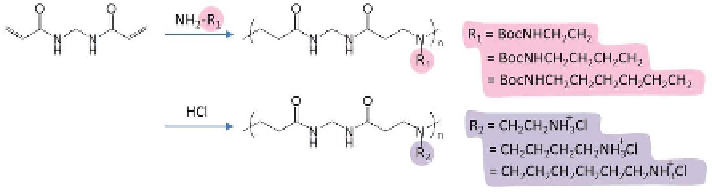
Scheme 4.15
Synthesis of a poly(amidoamine) with pendant primary amines.
nuclear localization than 25 kDa PEI. They also had much lower cytotoxicity
against BMSCs with an IC
50
of 100 mg mL
-1
. Based on previous research, Peng
et al. further investigated the biocompatibility, including in vitro cytotoxicity and
in vivo tissue compatibility.
113
The results demonstrated that these poly(amidoa-
mine) vectors possess much better cytocompatibility than 25 kDa PEI, yielding a
slight cell morphological change, high cell viability, and a mild effect on cell
membrane damage. They also exhibited better tissue compatibility, reflected by
no or less inflammatory response in the site of muscle injection.
Liu et al. synthesized novel poly(amidoamine)s with pendant primary
amines by Michael polyaddition of a diamine to N,N-methylenebis(acryla-
mide) (Scheme 4.15).
114
These polymers all showed high buffering capacity
between pH 5-7 and excellent DNA binding ability, which can condense DNA
to form nanosized polyelectrolyte complexes with a positive surface charge.
These
polymers
had
comparable
transfection
efficiency
and
much
lower
cytotoxicity than that of commercial 25 kDa PEI.
4.6.4
Multi-layer Complexes
Binary complexes of cationic polymers and DNA have been used commonly for
DNA delivery, but the excess cationic charge of the binary complexes mainly
leads to high toxicity and instability in vivo. In attempting to shield the cationic
charge and reduce the cytotoxicity, various multi-layer complexes have been
designed. Cheng and colleagues prepared a series of self-assembled polyionic
complexes (PICs) via electrostatic attraction between protamine sulfate (PS) and
poly(
L
-aspartic acid) [P(Asp)] or doxorubicin (DOX)-conjugated P(Asp).
115
An
in vitro gene transfection investigation revealed that the transfection efficiency
of the PICs/DNA complexes was comparable to that of 25 kDa PEI/DNA
complex (N/P ratio 5 10). Importantly, the gene transfection efficiency of PICs/
DNA complexes could be tuned by altering the weight ratio of PS/P(Asp). The
suppression of the proliferation activity of HeLa cells could be achieved by
replacing P(Asp) with DOX-P(Asp), suggesting a great potential of PICs as
effective carriers for combined delivery of drug and gene.
Guo et al. developed ternary complexes by coating polyglutamic acid-graft-
PEG (PGA-g-mPEG) onto binary complexes of polycaprolactone-graft-poly
(N,N-dimethylaminoethyl
methacrylate)
(PCL-g-PDMAEMA)
nanoparticles