Hardware Reference
In-Depth Information
GPS tutorial
The
Global Positioning System
(
GPS
) is a system of satellites that transmits signals. GPS
devices use these signals to calculate a position. There are a total of 24 satellites that trans-
mit signals all around the earth at any given moment, but your device can only see the sig-
nal from a much smaller set of satellites.
Each of these satellites transmits a very accurate time signal that your device can receive
and interpret. It receives the time signal from each of these satellites, and then, based on the
delay (the time it takes the signal to reach the device), it calculates the receiver's position
using a technique called triangulation.
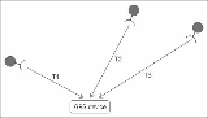
The following two diagrams illustrate how the device uses the delay differences from three
satellites to calculate its position:
The GPS device is able to detect the three signals and the time delays associated with re-
ceiving these signals.
Note
Time delay refers to the time difference between the travel time of each of these three sig-
nals.
In the following diagram, the device is at a different location, and the time delays associ-
ated with the three signals have changed: