Hardware Reference
In-Depth Information
Connecting a digital compass to Arduino
One of the important pieces of information that might be useful for your robot is its direc-
tion of travel. This could be given by a GPS unit, and we will cover how to connect one of
those in
Chapter 11
,
Using a GPS Device with Arduino
. However, a GPS unit can be ex-
pensive, and it often doesn't work well inside buildings, because the GPS satellite signals
don't penetrate buildings well. So, let's learn how to hook up a digital compass to Arduino.
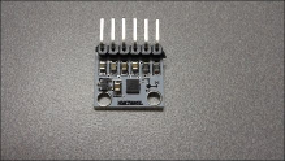
There are several chips that provide digital compass capability; one of the most common
ones is the
HMC5883L 3-Axis Digital Compass chip
. This chip is packaged onto a mod-
ule by several companies, but almost all of them result in a similar interface. Here is a pic-
ture of one by a company called SainSmart, and it is available at a number of online retail-
ers:
This type of digital compass uses magnetic sensors to discover the earth's magnetic field.
The output of these sensors is then made accessible to the outside world through a set of re-
gisters that allow the user to set things such as the sample rate and continuous or single
sampling. The x, y, and z directions are output using registers as well.
The connections to this chip are straightforward; the device communicates with Arduino
using the I2C bus, a standard serial communications bus.
Note
The I2C interface is a synchronous serial interface and provides more performance than an
asynchronous Rx/Tx serial interface. The SCL data line provides a clock, while the data
flows on the SDA line. The bus also provides addressing so that more than one device can
be connected to the master device at the same time.