Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
FAD [Franaszczuk et al., 1989] (Sect. 2.3.2.2.4). Namely, they decomposed the im-
pulse response function of the AR model into a sum of damped sinusoids. The very
low level of residual signal after fitting the AR model suggested that the recorded
PCG is essentially composed of delayed and overlapped repetitions of impulse re-
sponse function of the AR model.
Matching pursuit approach is a high resolution method of time-frequency analysis
(Sect. 2.4.2.2.7). It was applied by Zhang et al. [Zhang et al., 1998] for analysis-
synthesis of PCG. The dyadic dictionary with certain limitations imposed on scale
was used. The results showed that PCG can be synthesized from a limited number
of the highest energy atoms and the method acts as a powerful de-noising filter.
The separation of heart sounds from noise based on MP decomposition and fuzzy
detection was also applied in [Tang et al., 2010]. In a practical experiment, heart
sound signal was successfully separated from lung sounds and disturbances due to
chest motion.
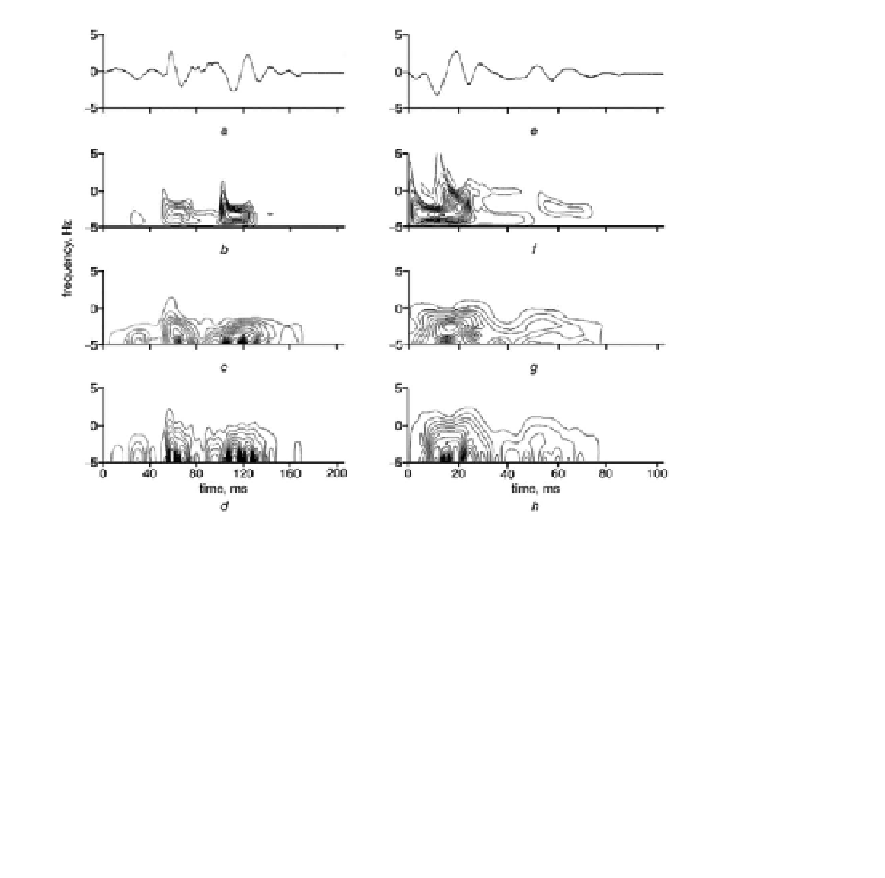
FIGURE 4.60:
Comparison of time-frequency distributions obtained by means of
MP and FT. (a) Averaged normal S1 of PCG and its contour plots using (b) MP-based
time-frequency distribution, (c) spectrogram with 64-point STFT window length,
and (d) spectrogram with 32-point STFT window length. (e) Averaged abnormal S1
of PCG and its contour plots using (f) MP-based time-frequency distribution, (g)
spectrogram with 64-point STFT window length, and (h) spectrogram with 32-point
STFT window length. From [Wang et al., 2001].






Search WWH ::

Custom Search