Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
considerably higher if it was run interactively by an operator. To resolve parts of the
EMG signal, presumably resulting from the overlapping MUAP waveforms, a two-
step procedure was applied. The template fitted in the first step was subtracted from
the signal. This produced a residue. In the second step, an attempt was made to fit
another template to the residue.
In the relatively simple semi-automatic system proposed in [Mazurkiewicz and
Piotrkiewicz, 2004] the first step of classification involved the criterion of similarity.
Construction of a similarity vector was based on cross-correlation between the given
MUAP and several templates indicated by an operator. In the next step the nearest
neighbor classification algorithm was applied. The decomposition of complex po-
tentials into superimposed MUAPs, based on consideration of the discharge rates of
units, was performed interactively. The correct classification rate varied from 60%
to 100% depending on the quality of the signal. The determined interspike intervals
trains were inspected in the context of estimating afterhyperpolarization duration
times of motoneurons. The results found application in the study of various neuro-
muscular disorders.
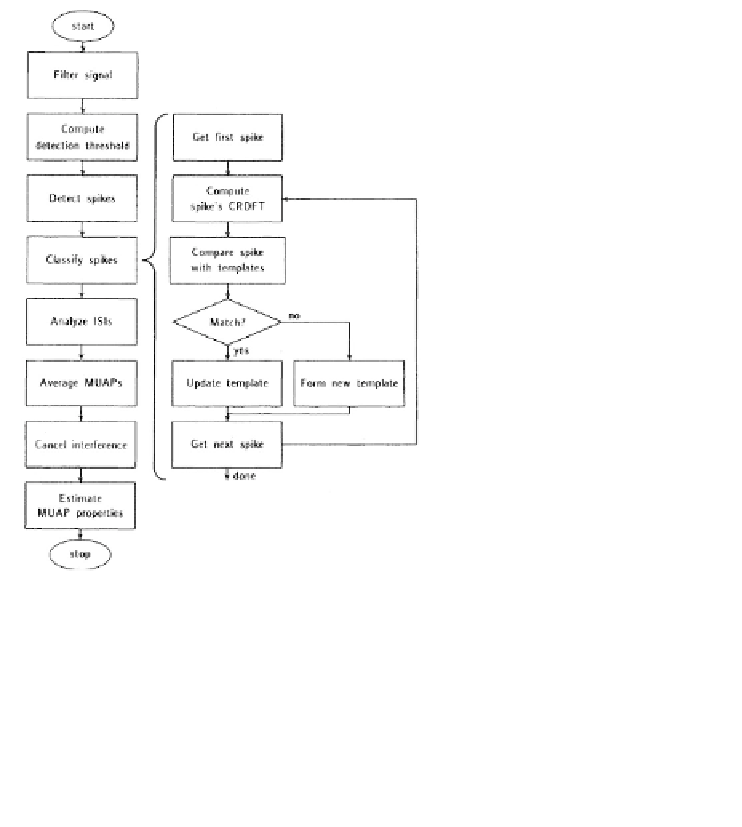
FIGURE 4.52:
Flowchart of ADEMG program. From [McGill et al., 1985].






Search WWH ::

Custom Search