Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
AFGHANISTAN
India
Soil loss
Jammu & Kashmir
50 0
350
km
Himachal Pradesh
Punjab
Uttaranchal
Haryana
DELHI
Arunachal Pradesh
Sikkim
BHUTAN
Uttar Pradesh
Assam
Rajasthan
Nagaland
Meghalaya
Bihar
Manipur
BANGLADESH
Tribura
Mizoram
Jharkhand
Madhya Pradesh
Gujarat
We st Bengal
Chhattisgarh
Orissa
Maharashtra
Andhra Pradesh
Legend
Moderate 10-15
Mod. severe 15-20
Severe 20-40
Very severe 40-80
Extr. severe >80
Wind erosion
Others
Area not covered in survey
Forest
Goa
Karnataka
Tamil Nadu
Kecala
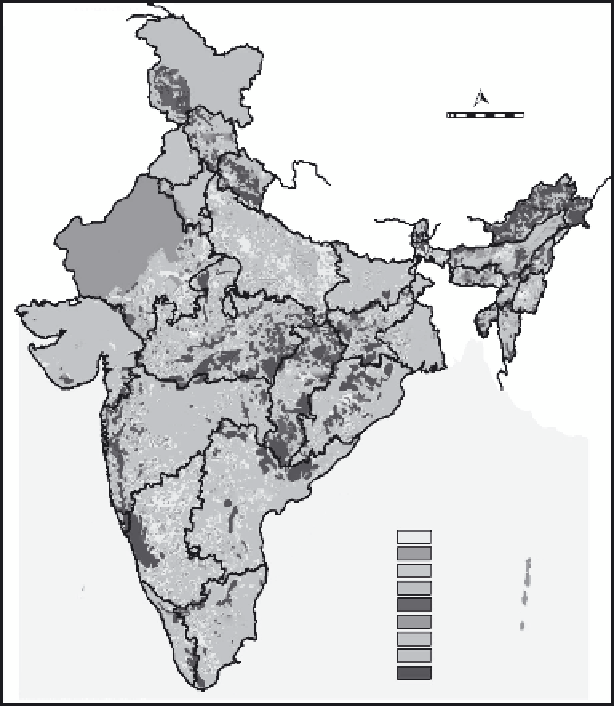
(b)
FIGURE 16.2 (Continued)
(a) Physical land degradation in India. (b) Soil loss by water ero-
sion (>10 Mg ha
-1
year
-1
). (c) Wind erosion in India (>10 Mg ha
-1
year
-1
). From Venkateswarlu,
B. et al.,
Natural Resource Management for Accelerating Agricultural Productivity
, Stadium
Press (India) Pvt. Ltd., New Delhi, India, 2012.)
16.3.5 U
ntapped
w
ateR
-n
UtRient
S
yneRgy
Rainfed regions often suffer from water scarcity and are characterized by multinutrient-
deficient soils. However, applying plant nutrients in synergy with profile moisture
storage is crucial in improving crop productivity and enhancing nutrient and water
use efficiencies.
16.3.6 p
ooR
c
Rop
M
anageMent
Untimely sowing, lack of weeding and supplemental irrigation, and suboptimum
plant population result in poor crop stand. Excessive weed infestation can smother
growth of the crops and severely reduce their productivity. Yet, a judicious crop
Search WWH ::

Custom Search