Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
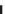
Fig. 13.7 The probability
P
=
P
{
K
=
k
}
of
k
frost-free years within
a period of
n
=
8
years at a location
where the probability
of a frost-free year is
estimated to be
p
=
26
/
45. (See
Example 13.4.)
0.3
P
0.2
0.1
0
0
2
4
6
8
k
the probability of 3, 4, or 5 successes, that is the sum of the probabilities of respectively
3, 4, and 5 successes, or
26
45
i
19
45
5
−
i
5
5!
i
!(5
P
{
K
≥
3
}=
−
i
)!
i
=
3
which equals 0.643.
13.4
SOME PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS FOR CONTINUOUS
VARIABLES
In flood and drought frequency analysis, the variable in question can usually assume
any value, so that, within certain limits, it can be considered as being continuous. In this
section some of the more common distribution functions are considered.
13.4.1
The normal distribution
This is a well-known function, but it is useful to consider it briefly, mainly as a reference
or benchmark to compare other less common distribution functions with it later on. The
normal or Gaussian density function has two parameters, namely the first two moments,
and it can be written as follows
exp
2
x
1
1
2
−
μ
σ
f
(
x
)
=
√
2
−
−∞
<
x
≤∞
(13.34)
σ
π
in which
is the standard deviation. This is a symmetrical bell-
shaped curve that extends from minus to plus infinity on the
x
-scale; thus its median,
μ
denotes the mean, and
σ