Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
1.5
x
+
=1
u
+2
and
u
+
1
5
0.5
10
x
+
=20
0
0
5
10
15
t
+
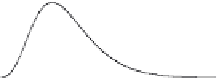
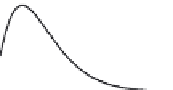
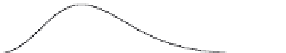
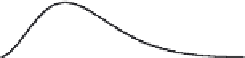
Fig. 5.9 Comparison between the unit response function
u
+
2
=
h
0
u
2
/
(
S
0
V
0
) for the upstream inflow
problem, obtained with the complete shallow water equations (solid line) and
u
+
=
(
S
0
V
0
)
obtained with the diffusion approximation (thin line). Each unit response curve is shown as a
function of time
t
+
at different distances
x
+
downstream from the release point of the unit
impulse. The constant is
a
=
2
/
3 and the Froude number is taken as Fr
0
=
0
.
5. The shallow
water results for
x
+
=
1
,
5 and 20 are the same as those shown in Figure 5.8.
h
0
u
/
An improved linear diffusivity
Equation (5.88) was derived here simply by neglecting the first two terms in the momentum
equation (5.22) and then linearizing. This way it can be seen that it is mainly the third
term in (5.22), namely
g
(
∂
h
/∂
x
), which is responsible for the diffusion character of the
resulting equation. Indeed, when this third term is also omitted, the resulting formulation
loses its diffusion character, as will be shown in Section 5.4.3. However, it should be
noted that this is not the only way to obtain a linear diffusion equation for free surface
flow. It is also possible to start from the complete linear system (5.67) and to modify
(rather than eliminate) the second derivatives involving time by means of the quasi-steady-
uniform flow or kinematic wave assumption (see Section 5.4.3; also Brutsaert, 1973). As
will become clear below (see Equation (5.118)) this assumption allows the substitution
(
∂
q
/∂
t
)
=
(
a
+
1)
V
0
[
−
(
∂
q
/∂
x
)
+
i
] in the second derivatives involving time in (5.67).
This leads then to a diffusion equation with a diffusivity, different from (5.89), namely
bq
0
S
0
1
−
a
2
Fr
0
D
0
=
(5.97)
or, for a channel of width
B
c
,
bQ
0
B
c
S
0
1
a
2
Fr
0
D
0
=
−
(5.98)
In the case of the upstream inflow treated in Example 5.7, the unit response (5.96) becomes
with this improved diffusivity
1
/
2
exp
−
[
x
+
−
1)
t
+
]
2
2
1
−
a
2
Fr
0
t
+
(
a
+
S
0
V
0
h
0
x
+
2
π
1
−
a
2
Fr
0
t
3
u
=
(5.99)
+