Java Reference
In-Depth Information
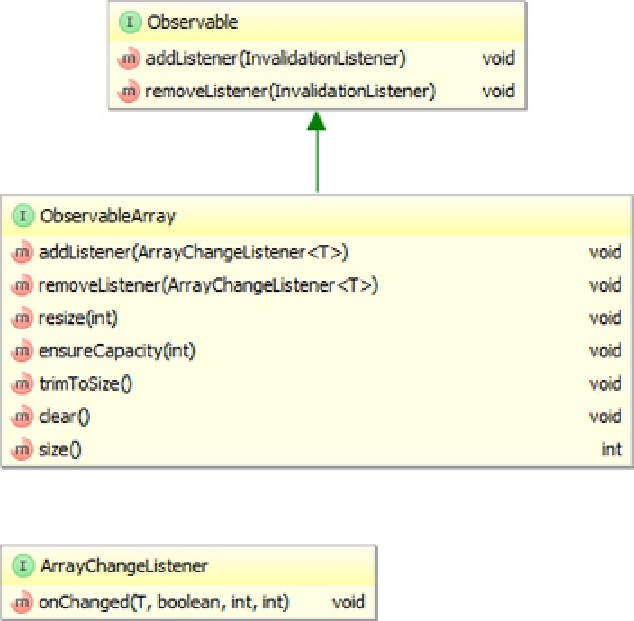
Figure 7-4.
Key interfaces that support the JavaFX observable array
Unlike for the
ObservableList
,
ObservableMap
, and
ObservableSet
interfaces, the
ObservableArray
interface
does not implement any Java collections framework interfaces. The following methods on the
ObservableArray
interface allow you to register and unregister
ArrayChangeListeners
:
addListener(ArrayChangeListener<T> listener)
•
removeListener(ArrayChangeListener<T> listener)
The following additional methods on
ObservableArray
give you control of the underlying primitive arrays:
•
resize(int size)
•
ensureCapacity(int capacity)
•
trimToSize()
•
clear()
•
size()
These methods deal with the capacity and size of an
ObservableArray
. The
capacity
is the length of the underlying
primitive array. The
size
is the number of elements that actually contain application data. The capacity is always greater
than or equal to the size. The
ensureCapacity()
method allocates a new underlying primitive array if the length of
the current underlying primitive array is less than the desired new capacity. The
resize()
method changes the size of
ObservableArray
. If the new size is greater than the current capacity, the capacity is increased. If the new size is greater
than the current size, the additional elements are filled with zero. If the new size is less than the current size,
resize()
does not actually shrink the array, but the “lost” elements are filled with zero. The
trimToSize()
method replaces the
underlying primitive array with one whose length is the same as the size of the
ObservableArray
. The
clear()
method
resizes the
ObservableArray
to size zero. The
size()
method returns the current size of the
ObservableArray
.
•
Search WWH ::

Custom Search