Geology Reference
In-Depth Information
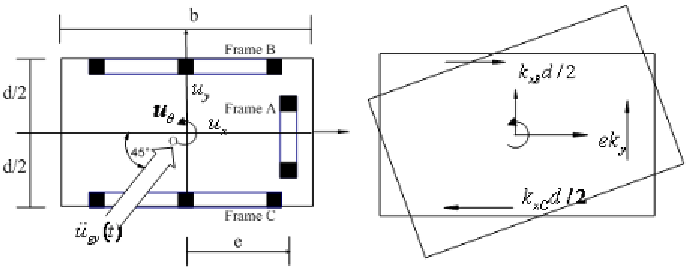
Figure 10. Stiffness of two-way asymmetric system (Chopra 2000)
where
M
is the seismic mass matrix of the
20-story building and
b
and
d
are the distances of
structural plan of the NS- and EW-directions,
respectively. Finally, the governing equation of
motion is
output,
y
r
is the vector of regulated responses,
v
is a measurement noise vector, and
C
r
, D
r
,
and
F
r
depend on the sensor locations and the number of
actuators and locations, and
0
I
,
(23)
ndof ndof
×
ndof ndof
×
A
=
−
M x +C
x + K
x =
M
−
1
K
−
M
−
1
C
3D20s
3D20s
3D20s
3D20s
3D20s
ndof ndof
×
3D20s
3
D20s
ndof ndof
×
(19)
- M G
x
g
+ P
f
3D20s
3D20s
3D20s 3D20
s
0
where
K
3D20s
(60x60) is the global stiffness ma-
trix,
M
3D20s
(60x60) is the global mass matrix,
C
3D20s
(60x60) is the global damping matrix that
is defined by 2% proportional Rayleigh damping,
G
3D20s
is ground motion matrix,
P
3D20s
is a loca-
tion vector of the control device forces, and
f
3D20s
is the control force input. The 2
nd
order differen-
tial equations can be transformed into the 1
st
order
state space equations
ndof ndof
×
B
=
,
(24)
-1
M
f
”
3D20s
a
ndof ndof
×
I
0
ndof ndof
×
ndof ndof
×
,
C
=
0
I
m
3 3
×
ndof ndof
×
−
1
−
1
−
M
K
−
M
C
3D20s
3D20s
ndof
×
ndof
3D20s
3D20s
ndof ndof
×
(25)
0
0
ndof ndof
×
D
=
,
(26)
m
ndof ndof
×
x
=
Ax Bf
+
+
E
x
g
(20)
−
1
”
f M
(
)
a
3D20s
ndof ndof
×
y
=
C x D f
+
+
F
x
g
+
v
(21)
0
G
3D20s
m
m
m
m
ndof
×
1
E
=
−
,
(27)
ndof
1
×
x
g
y
=
x +C x D f
+
+
F
(22)
r
r
r
r
where
x
is the state vector,
f
is control force input,
y
m
is the vector corresponding to the measured
Search WWH ::

Custom Search