Geology Reference
In-Depth Information
developed using finite element models with
lumped seismic mass, Ritz method and static
condensation approach. The damping matrix is
defined by 2% proportional Rayleigh damping.
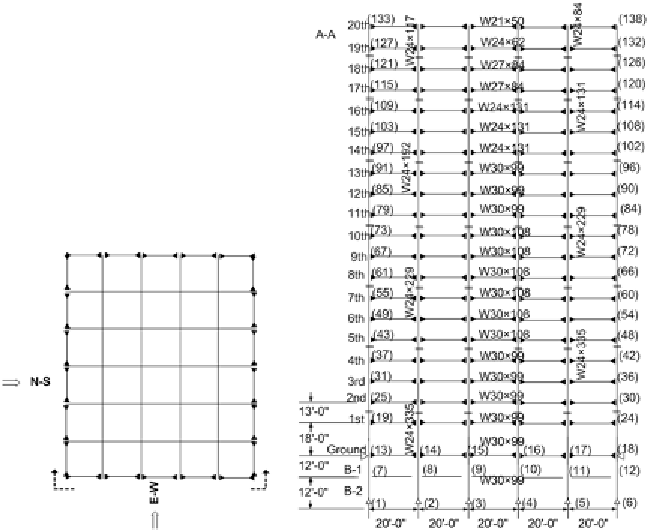
A 3D twenty-story frame structure with the reduced
60 DOFs is developed using the pre-determined
stiff and weak direction as shown in Figure 9. The
lateral and transversal stiffness are calculated to
eradicate zero mess degree-of-freedom (DOF).
The mass matrix
M
3D20s
is defined for the 3D
system as
d
are longitudinal and transverse length of struc-
tures, respectively. The stiffness matrix
k
story
of
each story is defined as (Chopra 2000)
k
+
k
0
( / )(
d
2
k
−
k
)
xB
xC
xC
xB
k
story
=
0
k
ek
y
y
( / )(
d
2
k
−
k
)
ek
e k
2
+
(
d
2
/ )(
k
+
k
)
xC
xB
y
y
xB
xC
(17)
where
k
xB
,
k
y
and
k
xC
are the lateral stiffness of
the frame B, A, and C, respectively;
d
and
e
are
the distances from the center of axis to each frame
as shown in Figure 10; and the stiffness matrix
k
story
is extended into a global stiffness matrix
K
3D20s
. The moment of inertia of the diaphragm
about the vertical axis passing through
O
in Fig-
ure 10 is determined by (Chopra 2000)
2
M
0
0
x
M
3D20s
=
0
2
M 0
(16)
y
0
0 M
r
where
M M
x
=
is the 20x20 seismic mass
matrix in weaker and stiffer direction of 3D struc-
tures and
M M
r
2
2
=
x
b
(
+
d
) /
12
where
b
and
2
2
I M
o
=
(
b
+
d
) /
12
(18)
Figure 9. Three-dimensional twenty-story building model
Search WWH ::

Custom Search