Geology Reference
In-Depth Information
BIO-INSPIRED SMART
CONTROLLER
hybrid neuromorphic smart controller for vibration
mitigation of seismically excited structures
equipped with magnetorheological dampers.
Neuromorphic Smart
Control Formulation
Brain Emotional Learning (BEL) Model
The brain limbic system is an organ that is related
to the emotional processing mechanism inside the
mammalian brain. The limbic system is closely
related to the functions of memory, emotional
processing, and emotional learning (Picard 1997).
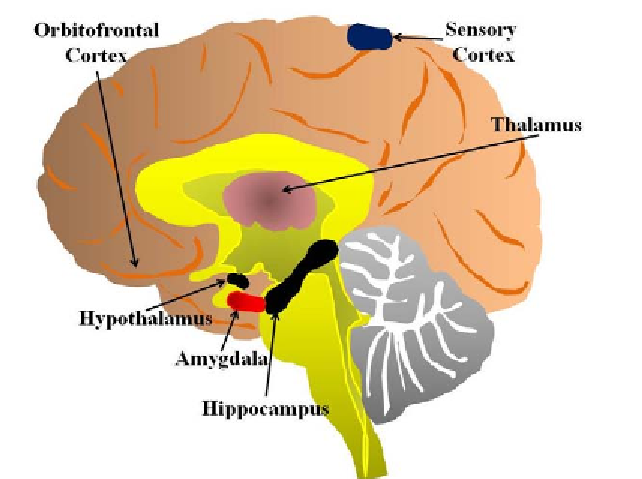
The anatomical structure of the human limbic
system is shown in Figure 1.
The main components of brain limbic system
are amygdala, orbitofrontal cortex, sensory cortex,
and thalamus. This part of brain is involved in the
emotional processing and learning (Bechara et al.
2000; Rolls 2000). In what follows, the primary
components of the brain limbic system are
briefly described and then a mathematical model
of brain limbic system is introduced. Finally, the
mathematical model is integrated with a PID and
a semiactive inversion algorithm to develop a
A mathematical relationship between the com-
ponents of brain limbic system was proposed by
Moren and Balkenius (2000) from the descriptive
physical model of the limbic system that provides
a qualitative sense of the overall functioning of
the system. Figure 2 shows the structure of the
Moren-Balkenius' computational BEL model. As
depicted in the figure, the BEL model has four
components of the so-called limbic system of the
brain: amygdala, orbitofrontal cortex, sensory
cortex and thalamus. Of them, amygdala and or-
bitofrontal cortex perform an important function
in emotional processing (Moren and Balkenius
2000).
The basic idea behind the BEL-based control
strategy is to generate reaction (or control output)
that maximizes the emotional reward (or mini-
Figure 1. A schematic of brain limbic system
Search WWH ::

Custom Search