Geology Reference
In-Depth Information
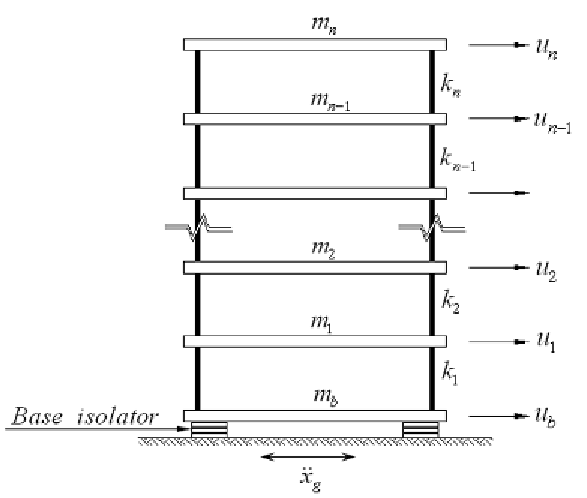
Figure 2. Mathematical model of N-story base-isolated building structure (Pourzeynali & Zarif, 2008).
denotes to the time derivative. While for a seismi-
cally isolated structure with the base mass
m
b
the
governing equation of motion of the building
alone can be written as (Naeim & Kelly, 1999):
where
n
is the number of stories of the building;
k
b
and
c
b
are the stiffness and damping of the base
isolator system;
m
i
is the mass of the building ith
story; and m
b
is the mass of the base slab.
This procedure of modeling the base isolated
building is valid for linear behavior of the isolator
systems given in detail by Kelly (1996).
By combining Equations (6) and (7) the general
equation of motion of the combined seismically
isolated building structure and the base slab, in the
matrix format, can be expressed as the following
(Naeim & Kelly, 1999):
(
)
(6)
M V
+
C V
+
K V
= −
M R x
+
v
{ }
{ }
{ }
{ }
g
b
where {
V
} is the displacement vector of the build-
ing stories relative to the base slab; and
v
b
is the
relative displacement of the base slab with respect
to the ground. As well, the overall equation of
motion of the combined building and base slab
can be written as follow (Naeim & Kelly, 1999)
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
M V
+
C V
+
K V
= −
M R x
g
(8)
{
}
{
}
{
}
{
}
n
∑
T
{ }
R M V
{ }
+
(
m m v
+
)
+
in which
i
b
b
(7)
i
=
1
n
∑
{ }
c v
+
k v
= −
(
m m x
+
)
T
T
{ }
{ }
m
R M
T
c
0
k
b b
b b
i
b
g
M
*
=
s
,
C
*
=
,
K
*
=
b
b
{ }
{ }
{ }
M R
M
i
=
1
0
C
0
K
1
v
V
n
∑
1
*
*
b
R
=
{ }
,
V
=
{ }
m
=
m
+
m
0
s
b
i
i
=
(9)
Search WWH ::

Custom Search