Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
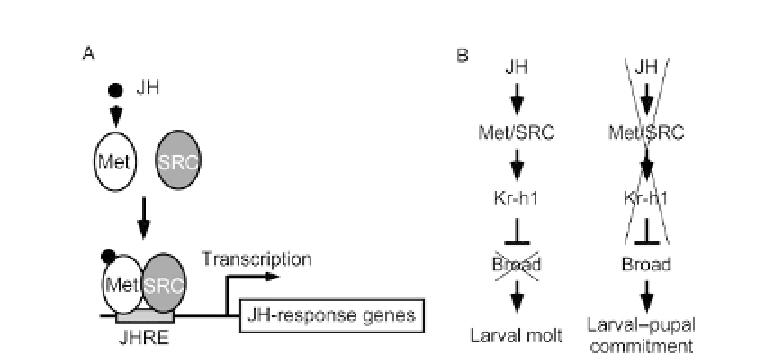
Figure 3.5 Model for Met as a JH receptor in insects (A) and JH signaling pathway
during larval
-
pupal commitment (B). JHRE, JH response element. See text for detailed
explanations.
signaling pathway downstream of the hormone's interaction with its receptor.
Consistent with this, when
Met
gene expression was suppressed,
Kr
-
h1
gene
expression was also suppressed (
Li et al., 2011; Minakuchi et al., 2009;
Zhu et al., 2010
). Kr-h1 is not only a crucial factor for JH control of larval
molting but is also induced by ecdysteroid and interacts with other genes such
as
broad
(
Beck,Pecasse,&Richards,2004
), SRC (
Zhang et al., 2011
), and
FISC (
Li et al., 2011
).
The induction of
broad
expression by ecdysteroid does not occur until
pupal commitment has been performed (
Zhou, Hiruma, Shinoda, &
Riddiford, 1998
), and its ectopic expression in early second instar
Drosophila
larvae before the rise of ecdysteroid titer prevented molting to the third
instar, but caused precocious pupae (
Zhou, Zhou, Truman, & Riddiford,
2004
). These results show that
broad
is one of the ecdysteroid-induced genes
that both specify pupal development and mediate the prevention of the
pupal-adult transformation (
Zhou & Riddiford, 2002; Zhou et al., 2004
).
RNAi suppression of
Met
or
Kr-h1
expression by dsRNA stimulates
broad
expression so that precocious metamorphosis results (
Konopova & Jindra,
2008; Minakuchi et al., 2009
); it, therefore, appears that Met bound to
JH stimulates Kr-h1 expression, thereby suppressing
broad
expression so that
the larval state is maintained (
Fig. 3.5
B).
Met/SRC and Met/FISC are required for the expression of JH respon-
sive genes including Kr-h1 (
Li et al., 2011; Zhang et al., 2011
), and SRC is
required for the expression of ecdysteroid-responsive genes. Therefore,
these factors as well as
broad
might mediate cross talk between JH and
ecdysteroid to prevent
the ecdysteroid-induced switch necessary for
metamorphosis.