Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
A
C
piRNA pathways
miRNA pathway
B
endo-siRNA pathway
in mammals
in
Drosophila
in
Drosophila
RNA polymerase II
dsRNA fragment
Long ssRNA
m7
Cleavage
Gppp
Dicer-2
Loqs
Drosha
pri-miRNA
DGCR8
Transposon mRNA
Piwi/Aub
AAAA
Dicer-2
Exportin5
Ago loading
complex
Dicer-2
Dicer
pre-miRNA
R2D2
ping-pong
cycle
Piwi/Aub
TRBP
Ago3
miRNA/miRNA*
duplex
Dicer
Ago2
siRISC
Ago2
miRISC
AGO
Ago3
piRNA cluster transcript
Ago2
AAAA
Transposon mRNA
AAAA
m7
G
m7
G
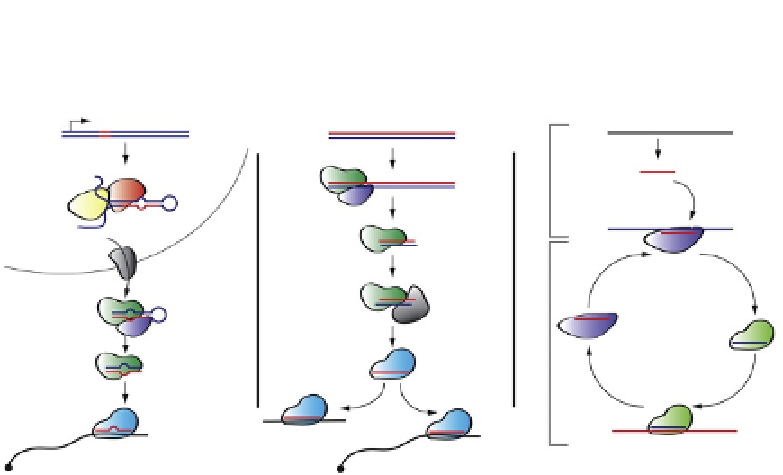
Figure 4.2
(A) Schematic representation of miRNA biogenesis and function in mam-
mals. miRNAs are transcribed by RNA polymerase II, and Drosha and DGCR8 process
the stem loop-containing pri-miRNAs. After export into the cytoplasm by Exportin 5,
Dicer and the accessory protein TRBP/Loqs (mammals/fly, respectively) further pro-
cess the pre-miRNA into the miRNA/miRNA duplex. The guide strand is then loaded
onto the effector protein AGO forming the miRISC complex that is guided toward the
3
0
UTR of the target mRNAs, resulting in deadenylation or translational repression.
(B) endo-siRNA biogenesis and function in D. melanogaster. Precursor double-stranded
RNAs (dsRNAs) fragments are processed by Dicer-2 and the dsRNA-binding protein
Loqs. The processed RNA bound to the R2D2 and Dicer-2 proteins is loaded onto
Ago2 forming the siRISC that targets the slicer activity of Ago2 toward target mRNAs
and RNA of transposable elements. (C) piRNA biogenesis and function D. melanogaster.
The single-strand RNA which is the precursor for piRNAs is cleaved and the resulting
antisense piRNA is loaded onto Piwi/Aub protein and binds transposon RNA thereby
initiating the ping-pong cycle. Cleavage of the transposon RNA generates a small sense
RNA molecule that is loaded onto Ago3 protein and the RNA-protein complex then
binds the piRNA transcript. Cleavage by piRNA/Ago3 and interaction of the resulting
small RNA with PIWI/Aub protein completes the cycle, leading to an increase in the
number of piRNA molecules and inhibition of transposon function.
(3
0
UTR). Association of miRNAs with their target commonly leads to
deadenylation and subsequent degradation of the target and can also result in
translational repression (
Carrington and Ambros, 2003; Lai, 2002
; reviewed
in
Bartel, 2009; Kim
et al
., 2009; Krol
et al
., 2010
).
2.2. miRNA function during PGC specification
As mentioned above, PGC specification in the invertebrates
C. elegans
,
D. melanogaster
and in some vertebrates like
X. laevis
and
Danio rerio
follows
the preformation strategy that depends on maternally provided factors.