Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
The search for
let-
7 transcription elements identified a
cis
-acting
sequence called the temporal regulatory element, TRE, located 223 and
1064nt upstream from the two transcriptional start sites (
Fig. 1.7
;
Bracht
HBL-1
RE
3
¢
ss
let-7
poly A
TRE
Transcription
and splicing
HBL-1
pri-let-7
SL1
AAAAA
Processing
XPO-1
CBC
LIN-28
pre-let-7
Processing
AIN-1/2
LIN-41
ALG-1/2
XRN-1/2
mature
let-7
RPS-14
NHL-2
AIN-1/2
Target
regulation
ALG-1/2
AAAAA
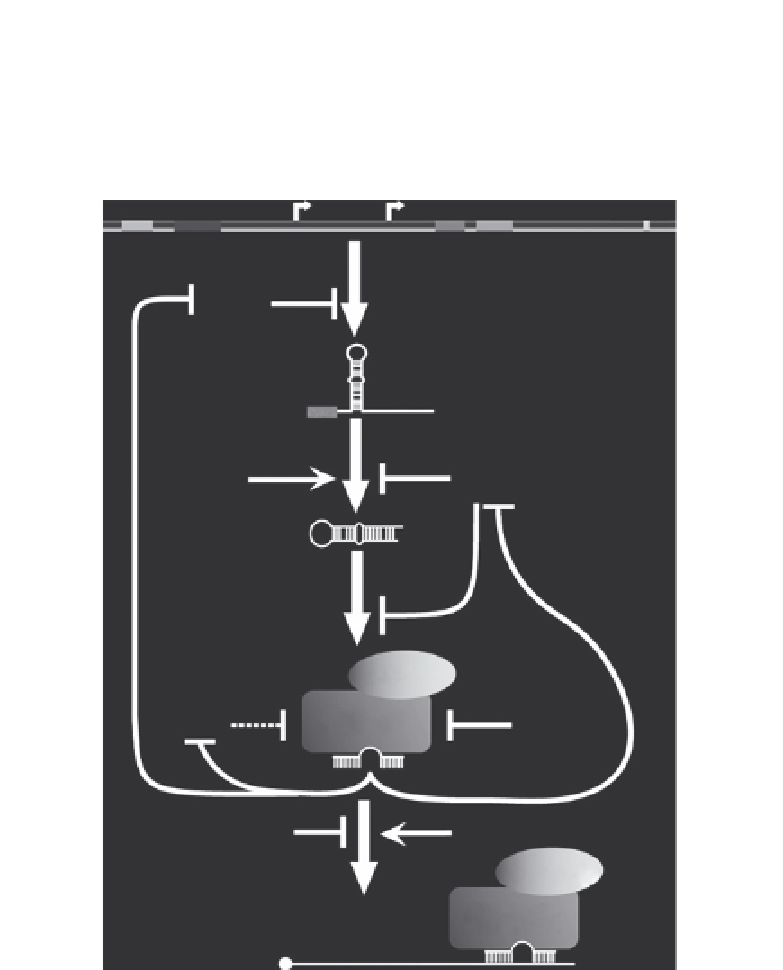
Figure 1.7
Regulation of let-7 biogenesis and function in C. elegans. Two cis-acting
elements in the let-7 promoter, the temporal regulatory element (TRE) and putative
HBL-1 response element, repress transcription in hypodermal seam cells. Two tran-
scription start sites produce primary transcripts that are polyadenylated and subject to
trans-splicing by the spliced leader 1 RNA (SL1) at the 3
0
splice site (3
0
ss) found
upstream of the mature let-7 sequence. The nuclear transport factors XPO-1 and
CBC promote conversion of primary to precursor and mature, while LIN-28 blocks
processing of primary and precursor RNAs. The 3
0
!
5
0
exonucleases XRN-1/2 degrade
mature miRNAs upon release from the Ago complex. LIN-41, a target of let-7,
indirectly regulates mature let-7 levels by targeting Argonaute for degradation in
mouse cells (a dashed line represents this step since this LIN-41 activity has not yet
been demonstrated in worms). As interactors with the Ago complex, NHL-2 enhances
repression of let-7 targets, while RPS-14 antagonizes let-7 function.