Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
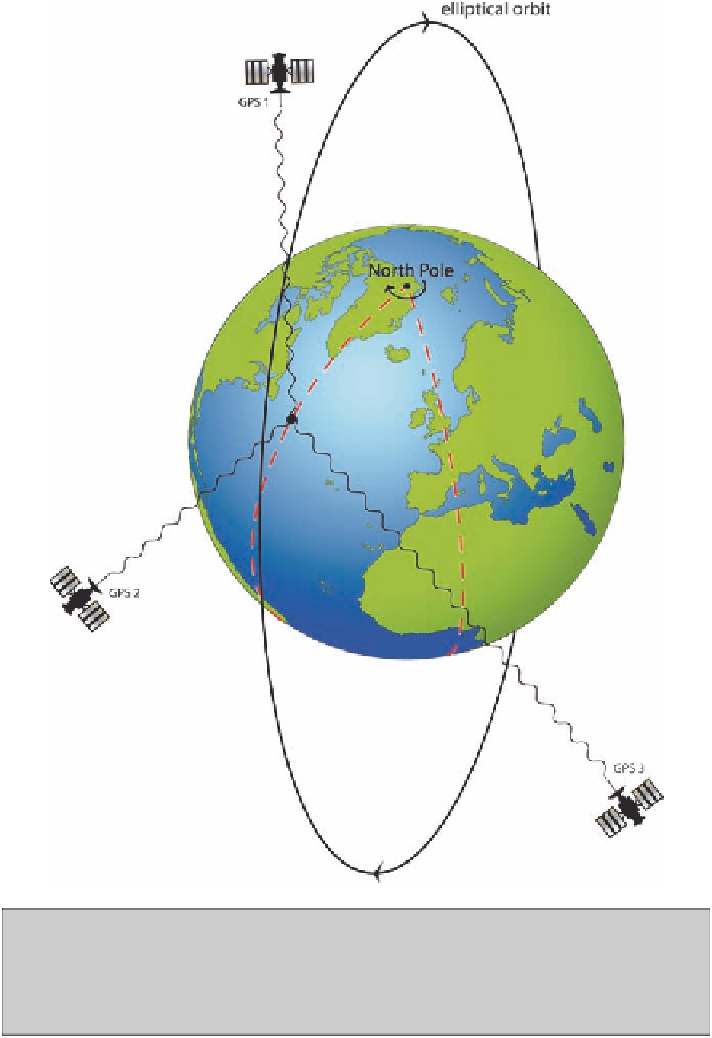
Fig. 37
A satellite navigational system like GPS measures the position of the receiver from
the signals sent by three of the swarm of satellites. Time delays between the transmission of
the signals and their reception at the receiver provide the location of the receiver relative to the
satellites. The receiver calculates the positions of the satellites from a second set of signals that
each broadcasts and locates itself on the surface of the Earth, relative to them
to the satellites (
Fig. 37
). There is more than one system in existence, including one
operated by Russia under the name GLONAST, but the system most widely used is
a formation of American space satellites called the Global Positioning System
(GPS). Stimulated particularly by France as a counter to American domination and