Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
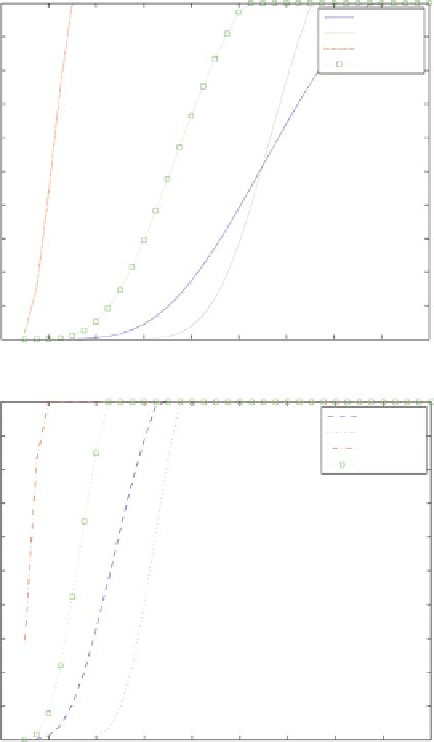
Fig. 16.9
Cylindrical metal
tanks for storing oil in
industrial plants: (
a
) Multi
failure modes = large size
tanks; (
b
) Multi failure
modes = small size tanks
a
Failure probability of tank h
tot
=19 R
tot
=10 cov alfa3=0.35 mean alfa3=0.8
1
P
f
buoyancy3
P
f
overturning3
P
f
sliding3
P
f
buckling3
0.9
0.8
0.7
0.6
0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.1
0
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
14
16
18
h
w
b
Fragility curves: Tanks: H[m]=8 R[m]=5.7...Filling level alfa3: c.o.v.=0.35 mean=0.8
1
P
f
buoyancy3
P
f
overturning3
P
f
sliding3
P
f
buckling3
0.9
0.8
0.7
0.6
0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.1
0
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
14
16
18
Wave height: h
w
[m]
16.3
General Conclusions and Discussion
Resilience analysis requires prior definition of utility functions, and their upper and
lower limiting values, as well as the reference period for a system's recovery, resto-
ration or transformation. Furthermore, recovery as well as disaster mitigation rely
on a relevant, accurate analysis of the system's vulnerability to potential hazards,
such as flooding and tsunami.
In the case of informal masonry constructions, 14 governing parameters have
been selected in order to define the mechanical vulnerability of the constructions
under the effect of floods. The theoretical fragility curves that have been developed
express the structural damage in masonry constructions
vs.
flood height and velocity;
Search WWH ::

Custom Search