Geology Reference
In-Depth Information
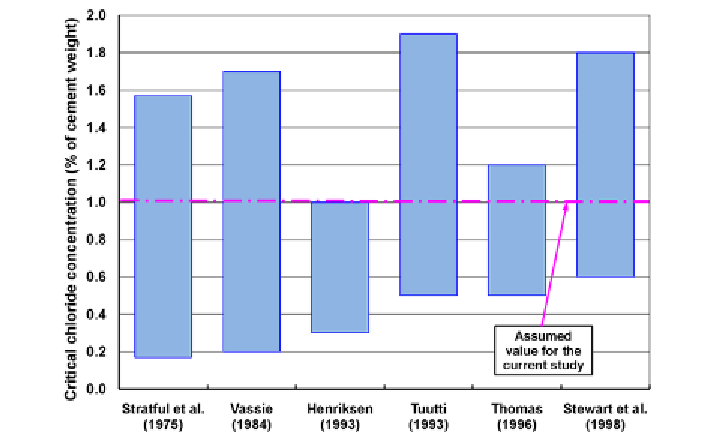
Figure 2. Summary of data available in literature for the critical chloride concentration required to
initiate the corrosion process
isotherms result in some change in the estimation
of the corrosion initiation time, which indicates
the importance of a reasonable choice for the
chloride binding model. The initiation time for
different cover depths of 40, 50, and 60 mm would
respectively be 7.23, 10.40, and 14.20 years
(Figure 3). It can be seen that the values of cor-
rosion initiation time obtained from the developed
algorithm lie well within the range of 7 to 20
years, observed by Kong et al. (2002).
relates the mass of steel consumed over the time
to the amount of current that flows through the
electrochemical corrosion cell. The rate of mass
loss per unit length of bar subjected to the corro-
sion, Δ
M
loss
(gr.cm
-1
), for a time step of Δ
t
(sec)
can be described as:
( )
=
π
( )
∆
M t
k D t i
∆
t
(8)
loss
corr
where
D
(
t
) is the reduced diameter of reinforc-
ing bar during the corrosion process,
k
, the mass
transport coefficient equal to 2.893×10
-9
, and
i
corr
,
the current per unit area of the reinforcing bar. For
the
i
corr
in Equation 8, a range of 10 to 25 μA.cm
-2
has been suggested by Rodriguez et al. (1994).
This range corresponds to the high reinforcement
corrosion risk because it is larger than 1 μA.cm
-2
(Andrade et al., 1993). In the current study,
i
corr
is
assumed to equal 10 μA.cm
-2
. By taking the steel
mass density,
ρ
s
, equal to 7.8 (gr.cm
-3
), the change
in the volume of corroded steel, Δ
V
loss
(cm
3
.cm
-1
),
can be simply calculated from Δ
M
loss
. The reduced
rebar diameter after each time step of corrosion
is calculated as:
3. STRUCTURAL DEGRADATION
DUE TO CORROSION
After the corrosion initiation time, the protection
film of the reinforcing bar is depassivated and the
transport of iron ions starts. This results in the
formation of rust layers around the rebar during
the corrosion process. This process continues until
the volume of rust reaches a level that causes the
concrete to crack due to the excessive expansion
of rust layers. In this study the crack initiation
time is calculated using the Faraday's law which
Search WWH ::

Custom Search