Geology Reference
In-Depth Information
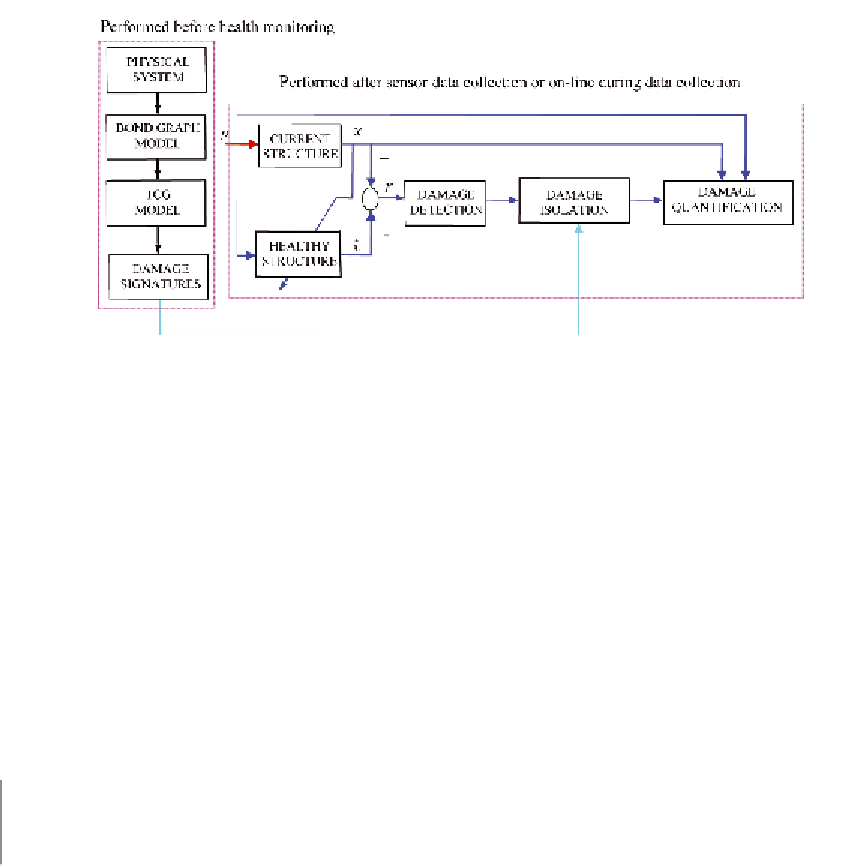
Figure 8. Damage identification for dynamic systems
8.3 Quantitative Damage
Identification
squares method to the substructure containing the
damaged floor only. This offers substantial savings
in the computational effort. For instance, if the
damage is isolated in the columns of the first or
the second floor we consider the substructure con-
taining the first two floors. Thus, the equations of
motion for the first two floors are given in Box 7.
These two equations can be recast in a matrix
form in Box 8.
The qualitative damage isolation described above
identifies the damaged component without quan-
tifying the damage size. For discrete structures
(i.e. the MDOF system that models a multi-story
building), the qualitative isolation identifies which
floor has damage. The damage size is quantified
by applying nonlinear optimization using the least-
Box 7.
m x t
( )
+
[
D
+
D x t
]
( )
−
D x t
( )
+ +
[
k
k x t
] ( )
−
k x t
( )
=
p
(
t
)
(17)
1 1
1
2
1
2 2
1
2
1
2 2
1
m x t
( )
−
D x t
( )
+
[
D
+
D x t
]
( )
−
D x t
( )
−
k x t
( )
+ +
k x t
[
k
]
( )
−
k x t
( )
=
p t
( )
2 2
2 1
2
3
2
3 3
2 1
2
3
2
3
3
2
Box 8.
D
D
D
1
2
x
x
x
0
x
x
x
0
x t
−
−
p t m x t
p t m
( )
−
−
( )
(18)
1
1
2
1
1
2
3
1
1 1
=
0
x
−
x
x
−
x
0
x
−
x
x
−
x
k
k
k
( )
2
( )
2
1
2
3
2
1
2
3
1
2
2
2
3






Search WWH ::

Custom Search