Geology Reference
In-Depth Information
4. ILLUSTRATIVE EXAMPLE
jective optimization where other conditions are
the same as Case B.
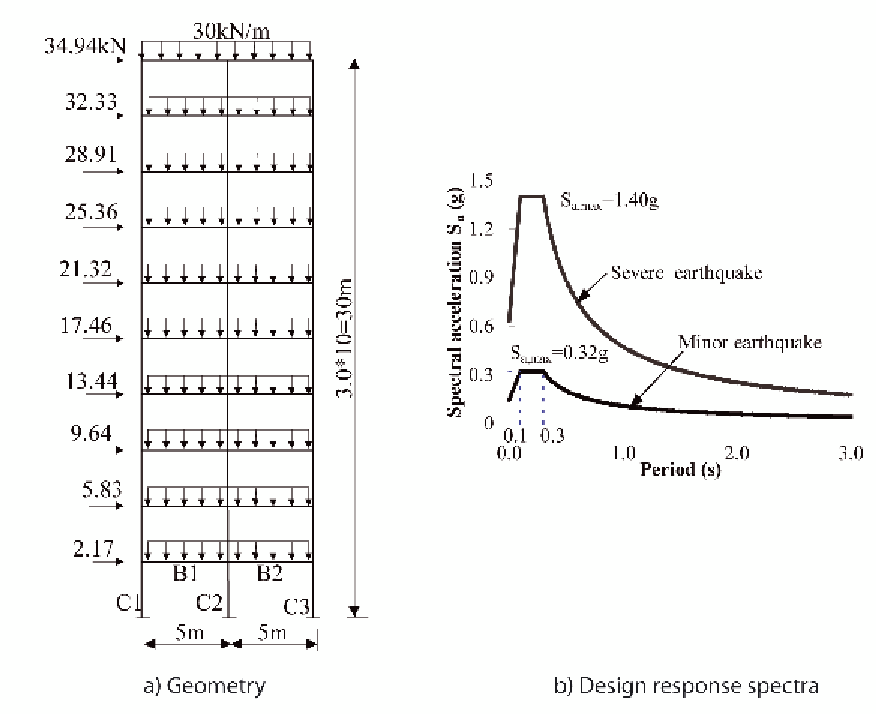
A ten-story, two-bay planar frame is used to il-
lustrate the proposed optimal design method. The
geometry of the example is given in Figure 4(a).
Concrete with the cylinder strength of 20MPa and
steel reinforcement with the yield strength,
f
y
, of
335MPa are used for all members. To illustrate
the effectiveness of the optimal design technique,
three cases are conducted in this example. Cases
A and B are elastic and inelastic design optimiza-
tion for a single objective, respectively, while
Case C considers life-cycle cost, i.e., multi-ob-
4.1 A Single Objective Optimization
(i.e., Cases A and B)
Two levels of earthquake loads are considered in
this example. One represents a minor earthquake
load with a peak acceleration of 0.32
g
according
to the acceleration response spectrum in GB5011-
2001(2001), as shown in Figure 4(b). Another
load level represents a severe earthquake with an
initial peak acceleration of 1.4
g
. In the elastic
phase of the optimization, the concrete cost of the
Figure 4. A ten-story, two-bay frame
Search WWH ::

Custom Search