Graphics Reference
In-Depth Information
as
u
rab
/
abc
. However, a little vector arithmetic
shows that these expressions simplify. For example, the expression for
rab
simplifies
as follows:
=
rbc
/
abc
,
v
=
rca
/
abc
, and
w
=
n
·
((
A
−
R
)
×
(
B
−
R
))
=
(original expression)
n
·
(
A
×
(
B
−
R
)
−
R
×
(
B
−
R
))
=
(expanding cross product)
n
·
(
A
×
B
−
A
×
R
−
R
×
B
)
=
(expanding cross products; removing
n
·
(
R
×
R
)
=
0
term)
n
·
(
A
×
B
−
A
×
(
P
−
t
n
)
−
(
P
−
t
n
)
×
B
)
=
(substituting R
=
P
−
t
n
for R)
n
·
(
A
×
B
−
A
×
P
+
tA
×
n
−
P
×
B
+
t
n
×
B
)
=
(expanding cross products)
n
·
(
A
×
B
−
A
×
P
−
P
×
B
+
t
n
×
(
B
−
A
))
=
(gathering similar terms)
n
·
(
A
×
B
−
A
×
P
−
P
×
B
)
=
(removing
n
·
(
t
n
×
(
B
−
A
))
=
0
term)
n
·
((
A
−
P
)
×
(
B
−
P
))
(contracting cross product after adding
n
·
(
P
×
P
)
=
0
term)
In other words, the barycentric coordinates of
R
can be obtained directly from
P
without computing
R
.
For
P
to lie in an edge Voronoi region — for example, the one corresponding to
edge
AB
—
P
would have to lie outside or on
AB
, signified by
rab
≤
0, as well as within
the positive halfspaces of the planes (
X
0.
Note that it is
not
sufficient just to test if
P
is outside
AB
, in that for a triangle with an
obtuse angle at
A
,
P
could be outside
AB
and actually be located in theVoronoi region
of edge
CA
(Figure 5.6). (Similarly, it is a common mistake to assume, for example,
that
A
is the closest point to
P
if
P
lies outside
AB
and (
P
−
A
)
·
(
B
−
A
)
=
0 and (
X
−
B
)
·
(
A
−
B
)
=
0.) If
P
is
not found to be in any of the vertex or edge Voronoi regions,
Q
must lie inside
ABC
−
A
)
·
(
B
−
A
)
<
P
A
C
B
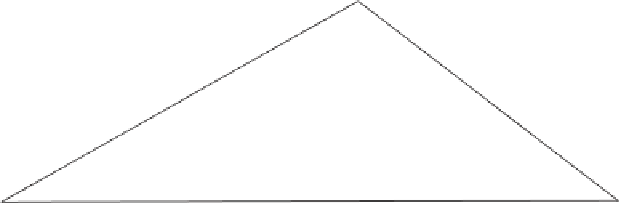
Figure 5.6
When the angle at
A
is obtuse,
P
may lie in the Voronoi region of edge
CA
even
though
P
lies outside
AB
and not in the vertex Voronoi regions of either
A
or
B
.