Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
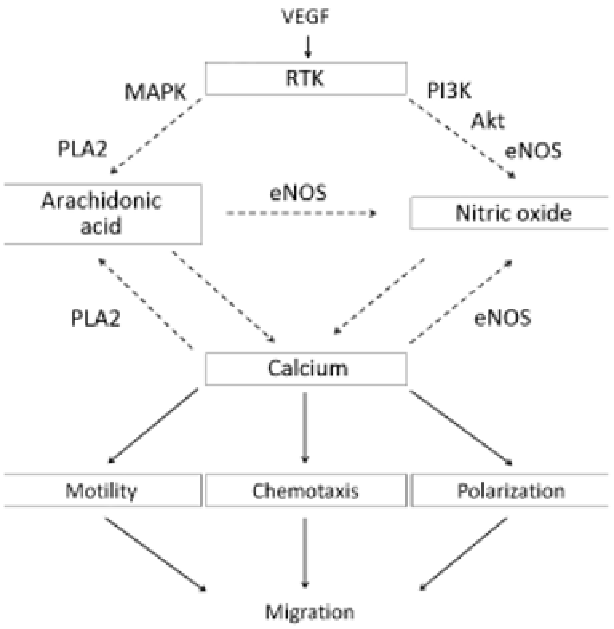
FIGURE 6.1: Simplified schematic representation of VEGF-induced
calcium-dependent events during chemotactic migration of a vascular endothe-
lial cell. VEGF molecules, binding to tyrosine kinase receptors, activate a series
of intracellular signalling inducing the recruitment of enzymes phospholipases
A2 (PLA2) and nitric oxide synthase (eNOS), and the subsequent produc-
tion of arachidonic acid (AA) and nitric oxide (NO), respectively. Both these
second messengers mediate calcium influxes from the extracellular environ-
ment through plasma membrane channels. Increases in the cytosolic calcium
level trigger cell intrinsic motility, cytoskeletal reorganization and chemical re-
sponse, crucial mechanisms for the regulation of cell migratory capacity. The
dashed arrows stand for indirect reactions, which are bundled in the model.
6.2 Mathematical Model
In the hybrid-nested modeling environment, a compartmentalized CPM rep-
resents at the mesoscopic, cellular level the phenomenology of the TEC indi-
vidual, while the microscopic biochemical VEGF-induced calcium-dependent









Search WWH ::

Custom Search