Geology Reference
In-Depth Information
HT3
Figure
38
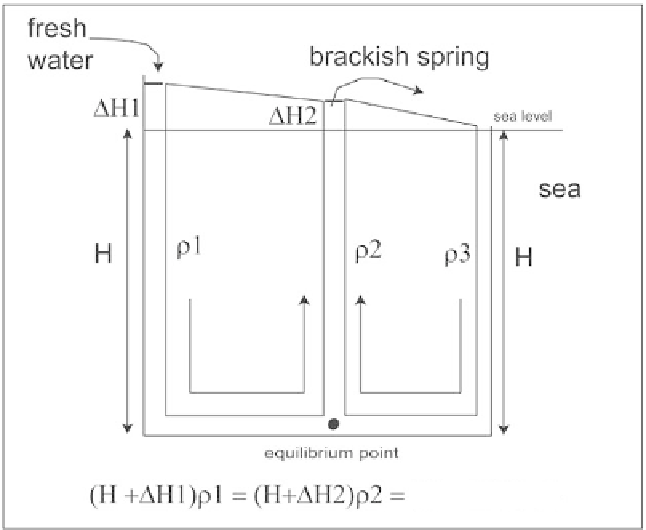
Inherited drain hypothesis.
A variation on this model was defi ned by Gjurašin (1943), called
diffl uence. It simplifi es the system to a karst drain dividing into two
branches at its end. The upper branch feeds the brackish spring; the lower
branch behaves like an estavelle. When the fresh water pressure becomes
large enough, the column of sea water is displaced, and the system is no
longer contaminated by seawater (Figure 39).
2.3.4 Concentrated versus diffuse contamination
The preceding models deal with well-individualised conduits, but nothing
prevents a situation where there is a diffuse contamination through the
network of fractures around a deep karst drain. Arfi b (2001) modelled
the Almyros at Iraklion. The model describes the workings of the spring
perfectly, by imagining a major drainage at a depth of 500 m, with diffuse
contamination around the drain. A Messinien emplacement is considered
likely, but there is also the possibility of tectonic tilting.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search