Geology Reference
In-Depth Information
After a detailed analysis of the geometric limits of the aquifer reservoir,
exploratory drilling found, at the heart of the graben, 120 m of Lower
Jurassic dolomite and limestone above Triassic formations, enclosing a rich
aquifer with a static water table at a depth of 25 m.
The exploitation borehole was drilled in 1993 and doubled in 1995,
in the graben's axis, at the elevation of 250 m a.s.l. After the creation of a
piezometer network along the length of the basin and along its edges, a
pumping test revealed a northern impermeable boundary, corresponding
to a strike-slip fault, and a clearly ovoid drawdown surface, the long axis
of which is aligned with the direction of the graben.
A prolonged emptying test was undertaken, and monitoring continued
during the exploitation of the catchments, based on a daily recording of
the piezometric level, the extracted volume, and the physico-chemical
parameters of the water (conductivity and hardness). Regular sampling
provided, in addition, an understanding of the evolution over time of the
pumped water (Figure 119).
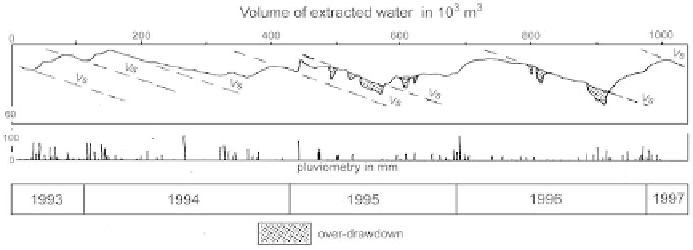
Figure 119
Pinchinade wells (Mouans-Sartoux, Alpes-Maritimes). Prolonged emptying test.
Sampling corresponds to the extraction of 950,000 m
3
in a little over
3 years. Analysis of the graph leads to the conclusion that the part of the
aquifer connected to the boreholes has a specifi c volume Vs of 4,000 m
3
·m
-1
,
and that the permanently exploitable resource has an estimated volume of
260,000 m
3
and a yearly renewable reserve of 270,000 m
3
.
Management of the resource nevertheless runs into limits, shown by
monitoring results, on both qualitative and quantitative levels:
from a quantitative aspect, it has been observed that when the extracted
discharge exceeds 1,000 m
3
.j
-1
(simultaneous pumping in both wells),
a sizeable increase in drawdown (on the order of 15 to 20 m) occurs,
which stops immediately as soon as the pumping rate decreases;
from a qualitative aspect, it has been observed that, during such
intensive pumping, the water chemistry is significantly altered,
demonstrated by a decrease in nitrate concentration (marker for
Search WWH ::

Custom Search