Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
these tags, an ear tag pliers is needed (Figure 12.5B). Make
sure the ear tags are inserted between the cartilage ribs of
the ear (Dawson, 2007a ; Dawson, 2007b ).
C
HALK
These are temporary markings and are used to sort animals.
Chalk will not stay on the goats for a long time. Usually
moisture or pressure (rubbing) will make the markings
disappear.
CASTRATION
Castration of male goats or kids is usually done during the
fi rst 7-14 days of their life. Castration of young animals
produces less stress because they are more tolerant to pain
at this age and have less chance of complications occurring
during this procedure. Castration is usually performed to
avoid undesirable odors associated with male goats,
aggressive sexual behavior, accidental breeding by a buck
of inferior quality, and to reduce undesirable fl avors in
meat in animals raised for meat purposes. However, this
procedure will reduce growth rate and increase the poten-
tial of urinary calculi in fatting kids used for meat. Also,
if the kid is used as a long-term pet or companion animal,
it is advisable to wait until the animal reaches puberty (4
months old), and then perform castration. This will allow
the growth of the penis and urethra, thereby reducing the
opportunity for urinary calculi. This will also enable the
penis to separate from the prepuce, thus enabling the vet-
erinarian to examine the penis, prepuce, and urethra if
needed. The two ways to castrate a goat are surgical and
nonsurgical (Dawson, 2007a; Dawson, 2007b).
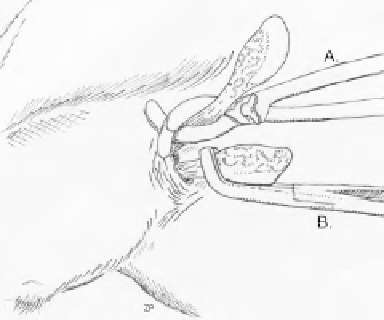
Figure 12.7
A: Spermatic cord crushed using an
emasculatome. B: Spermatic cord twisted using
a Henderson tool. Drawn by Zeke Proctor.
fi ngers up and down, while the other hand grasps the tes-
ticles and pulls it away from the animal's body. Once the
cremaster muscle has been separated from the spermatic
cord, the testicle is pulled or emasculated with an emascu-
lator (Figure 12.7A), or by using the Henderson tool on a
power drill to twist the cord till it breaks (Figure 12.7B).
This procedure is repeated on the other testicle. Any fat or
fascia hanging from the scrotum is trimmed even with the
bottom of the scrotum (Dawson, 2007b ; Hooper, 1998 ).
Nonsurgical Method
This method is usually performed with an elastrator or a
Burdizzo clamp. The author prefers mild sedation if used
on kids older than 2 weeks of age (Dawson, 2007a;
Dawson, 2007b ).
Surgical Method
This method is usually performed under supervision of a
veterinarian, with mild sedation under xylazine (or any
approved sedative drug for goats), and pain is managed
with fl unixin. A handler restrains the kid, while an expe-
rienced person performs the castration. Mud, dirt, and
manure are removed from the scrotum, and the area is
prepped with disinfectant prior to making an incision. The
scrotum is grasped with the forefi nger and thumb, and
stretched away from the animal's body. This forces the
testicles toward the body so that the bottom half of the
scrotum can be removed with a knife or scalpel blade
without cutting the testicles. The testicles are forced into
the open scrotum and grasped with one hand, while the
other hand is used to strip the fascia, fat, and cremaster
muscle surrounding the cord. This is best accomplished by
using the thumb and forefi nger of one hand to encircle the
cord, then stripping the spermatic cord by moving your
E
LASTRATOR
This procedure, sometimes called bloodless castration,
involves putting a heavy rubber ring around the neck of
the scrotum close to the body. The ring stops blood supply
to the testicles and scrotum that will later shrivel and
slough off in 10-14 days. Bigger testicles may take a long
time to slough off. The rubber ring is put on the prongs of
the elastrator, and the handle is squeezed to open the
prongs along with the band. The male kid is restrained, and
the scrotum with the testicles is passed through the open
ring with the prongs/band facing the kid's abdomen. Make
sure both of the testicles along with the scrotum pass
through the band and that the ring is positioned on the neck
of the scrotum just below the penis (Figure 12.8). Kids
usually show minimal discomfort for about 30 minutes to