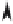Graphics Reference
In-Depth Information
Therefore,
n
=
i
+
j
and
c
=
1
Using Eq. (3.38),
c
−
n
·
p
1
−
2
=
=
=−
1
2
n
·
n
2
Using Eq. (3.39),
=
−
1
2
n
=
+
−
1
2
i
+
=
1
2
i
+
1
2
j
q
p
i
j
j
giving
Q
2
2
1
The distance
=
−
j
=
√
2
2
1
2
i
PQ
=
n
+
=
07071
Now let's consider the parametric form of the line equation.
3.8.2 The parametric form of the line equation
Y
P
T
r
λ
v
Q
v
p
t
q
X
Figure 3.21.
With reference to Fig. 3.21, let the straight-line equation be
q
=
t
+
v
(3.40)
The objective is to find the value of .
Q is the nearest point on the line to P with position vector
q
.
Because
r
⊥
v
,
p
, and
q
have identical projections on
v
, we find that
v
·
p
=
v
·
q
(3.41)