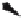Graphics Reference
In-Depth Information
B
B
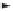
AB
BA
A
A
(b)
(a)
Figure 1.3.
If the line segment's arrow was pointing in the opposite direction, as shown in Fig. 1.3(b), it
would be labeled
−
BA. What, then, is the difference between the two line segments
−
AB and
−
BA?
Well, the distance between the points is the same; just the direction has changed, and we can
accommodate this difference by introducing a negative sign. For example,
−
BA
=−
−
AB
or conversely
−
AB
=−
−
BA
The effect of the minus sign effectively switches the letters labeling the points.
If we adopt this notation, the following statements are valid descriptions of other line
segments:
−
AC
=−
−
CA
and
−
−
BC
=
−
CB
The idea of following a path from one point to another is very useful when we begin solving
problems with vectors. Along this path we identify the line segments (vectors) that locate some
point, which eventually reveals the thing we are looking for.
Let's introduce a third point, C, and annotate the line segments as shown in Fig. 1.4.
B
BC
AB
C
AC
A
Figure 1.4.