Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
where the cardinality is given by
n
P
x
¦
P
x
.
Fi
Fi
1
1
i
1
The fuzzy
Jaccard index
complies with the four criteria described above, and
reflects the idea of gradual transition from equal to completely non-equal fuzzy
sets with S(
F
1
,
F
2
) = 0. This similarity is also used by Chao
et al
. (1996) for
training the structure of fuzzy artificial neural networks.
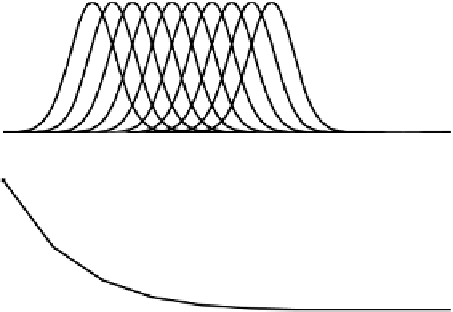
The similarity measure values for Gaussian fuzzy sets with a varying degrees of
overlap are shown in Figure 7.4. Figure 7.4(b) shows that degree of similarity
between the first Gaussian fuzzy set (GMF) and itself is 1.0, whereas it's degree of
similarity with the second fuzzy set from Figure 7.4(a) is only 0.4889, and with the
Gaussian MFs with varying overlap
1
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
0
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
(a)
GMFs with
varying deg. of
S
imilarity
1
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
(b)
Figure 7.4.
Gaussian fuzzy sets and varying degree of similarity
third Gaussian fuzzy set it is 0.2295, and so on. The list of degrees of similarity
between the first Gaussian fuzzy set and the fourth set and others are given as
follows: 0.1001, 0.0394, 0.0134, 0.0038, 0.0009, 0.0002, 0.0000.
7.5 Simplification of Rule Base
As discussed in Section 7.2, the automated approaches to fuzzy modelling
frequently introduce redundancy in terms of several similar fuzzy sets that describe
almost the same region in the domain of some model variable. These similarity
measures can be used to quantify the similarity between fuzzy sets in the rule base.
Two or more similar such fuzzy sets can be merged to create a new set to be stored
in the rule base as the representative of the merged sets. In this way, the overall























































































































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search