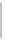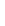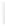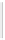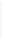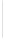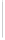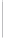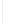Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
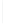
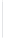
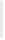
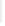
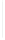
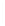
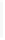
Figure 11-6
Determine the Router ID (Answer)
Fa0/1 192.168.1.65/26
Router ID:
192.168.1.65
RTA
Fa0/0 192.168.1.3/29
OSPF
Area 0
Fa0/1 192.168.1.193/26
Fa0/1 192.168.1.129/26
Fa0/0 192.168.1.1/29
Fa0/0 192.168.1.2/29
RTB
RTC
Router ID:
192.168.1.193
Router ID:
192.168.1.129
In Figure 11-6, which router would be the DR?
RTC
BDR?
RTB
You can override the router ID that OSPF chooses by configuring an IP address on a
loopback
interface.
This will provide stability to your OSPF network because
loopback
interfaces do not become inactive.
Assume that network policy has determined that RTA is best suited to be the DR. In addition, the policy
states that all OSPF routers will be configured with a loopback interface to provide stability to OSPF:
Loopback for RTA is 10.0.0.3/32
■
Loopback for RTB is 10.0.0.2/32
■
Loopback for RTC is 10.0.0.1/32
■
Document the correct commands, including the router prompt, to configure loopback interfaces on
each router.
RTA(config)#
interface loopback 0
RTA(config-if)#
ip address 10.0.0.3 255.255.255.255
RTB(config)#
interface loopback 0
RTB(config-if)#
ip address 10.0.0.2 255.255.255.255
RTC(config)#
interface loopback 0
RTC(config-if)#
ip address 10.0.0.1 255.255.255.255
With loopback interfaces now configured on each router, what must you do to change which router is
the DR?
The routers must either be reloaded or the OSPF process has to be removed with the
no router ospf
process-id
command and then completely reconfigured before routers will use the loopback addresses
as the router ID. However, the first router reconfigured will become the DR regardless of the value of
the router ID unless you reload the routers. So, the best way to ensure which router is the DR is by
configuring priority.