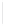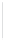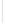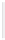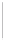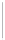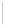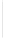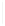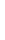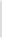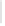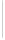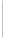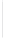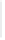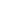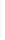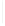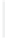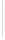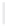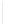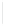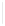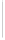Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
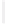
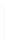
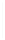
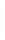
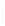
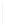
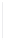
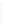
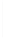
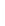
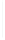
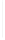
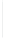
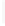
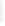
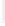
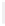
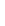
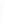
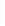
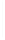
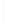
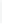
Figure 11-4
Establishing OSPF Adjacency
192.168.1.0/26
RTA
192.168.1.252/30
192.168.1.244/30
OSPF
Area 0
192.168.1.128/26
192.168.1.64/26
RTB
RTC
Using Figure 11-4, document the correct commands, including the router prompt, to configure
RTB and RTC to advertise all directly connected networks in OSPF.
!OSPF Configuration for RTB.
!Note that the process-id does NOT have to match with RTA
RTB(config)#
router ospf 2
RTB(config-router)#
network 192.168.1.64 0.0.0.63 area 0
RTB(config-router)#
network 192.168.1.244 0.0.0.3 area 0
9.
!OSPF Configuration for RTB.
RTC(config)#
router ospf 3
RTC(config-router)#
network 192.168.1.128 0.0.0.63 area 0
RTC(config-router)#
network 192.168.1.252 0.0.0.3 area 0
Verify OSPF Configuration Exercise
Fill in the missing commands to complete the following sentences.
The
show ip ospf neighbor
command can be used to verify and troubleshoot OSPF neighbor relation-
ships.
The
show ip protocols
command is a quick way to verify vital OSPF configuration information,
including the OSPF process ID, router ID, networks the router is advertising, neighbors the router is
receiving updates from, and default administrative distance, which is 110 for OSPF.
The
show ip ospf
command can also be used to examine the OSPF process ID and router ID.
Additionally, this command displays the OSPF area information as well as the last time the SPF algo-
rithm was calculated.
The quickest way to verify Hello and Dead intervals is to use the
show ip ospf interface
command.
The quickest way to verify OSPF convergence is to use the
show ip route
command to view the rout-
ing table for each router in the topology.