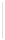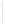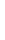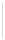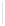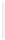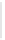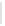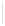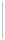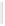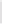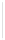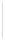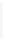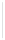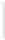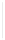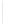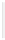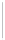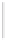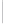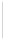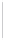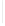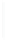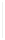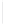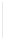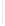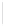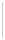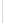Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
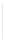
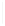
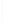
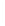
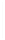
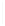
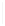
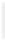
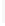
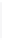
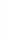
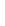
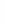
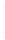
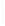
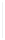
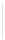
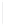
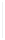
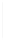
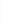
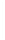
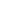
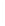
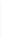
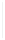
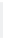
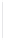
Figure 5-9
Topology with Default Routing
192.168.1.96/27
PC2
Fa0/0
R2
S0/0/1
DCE
RIPv1
S0/0/0
172.16.0.0/30
192.168.1.64/27
Static
Route
Default
Route
192.168.1.32/27
172.17.0.0/24
S0/0/0
DCE
S0/0/1
Fa0/0
Fa0/0
R1
R3
Internet
PC1
PC3
What commands do you need to enter on R2 and R3 to modify the topology for this configuration?
On R2:
Remove network 172.16.0.0 from RIP and set the S0/0/1 interface to passive.
R2(config)#
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 s0/0/1
R2(config)#
router rip
R2(config-router)#
no network 172.16.0.0
R2(config-router)#
passive-interface s0/0/1
On R3:
R3(config)#
ip route 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 s0/0/1
R3(config)#
no router rip
To provide Internet connectivity to all other networks in the RIP routing domain, the default static
route needs to be advertised to all other routers that use the dynamic routing protocol.
What command will configure R2 to propagate the default route to R1?
R2(config-router)#
default-information originate
Packet Tracer Exercise 5-2
Packet Tracer
Activity
Now you are ready to use Packet Tracer to configure default and static routing on the modified topol-
ogy in Figure 5-9. Open file LSG02-0502.pka on the CD-ROM that accompanies this topic to perform
this exercise using Packet Tracer.