Graphics Reference
In-Depth Information
5 Writedown a formula for
(
)
and find thesum
(
)
.
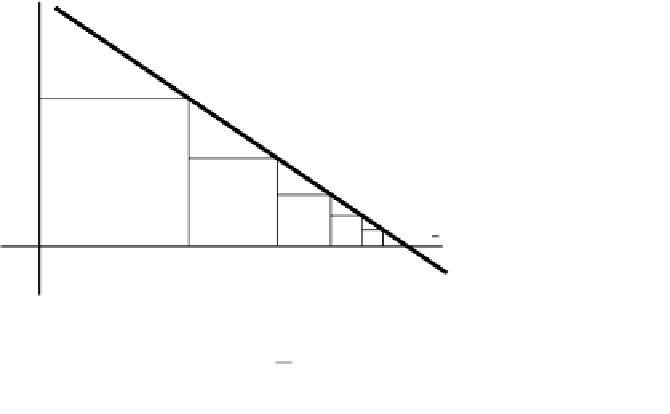
So, if you go half way, and then half of what is left, and then half
again, and so on, do you ever get there?
6 Find thesum
(
)
. What recurring decimal have you
evaluated?
7 Construct an infinite decimal equal to
.
8 Find thesum
(
)
.
9 Use qn 2 to determine whether the series
x
is convergent when
(i)
x
1,
(ii)
x
1.
Also examine the two cases
x
1 and
x
1.
1
1
x
x
2
1
x
r
2
10
(
Oresme
, c. 1350) If
s
show by induction or otherwise
that
s
.
Useqn 3.74 to deducethat (
s
2
(
n
2)/2
)
2as
n
. Comparewith qn
1.3(vii).
Oresme considered
1/2
....
There is a geometrical description of Oresme's proof in Kopp, p.
18.
1/2
1/2
Any series which is
not convergent
is said to be
divergent
. Thepartial
sums of a divergent series need not 'diverge' to
but may oscillate,
as with
(
1)
. When all the terms of a series are
positive
, the sequence
of partial sums is monotonic increasing: so, if the sequence is bounded,
the series is convergent; and, if it is not bounded, the series tends to
. See qn 25.