Hardware Reference
In-Depth Information
Network Topology
A Bluetooth Low Energy device can communicate with the outside world in two ways:
broadcasting
or
connections
. Each mechanism has its own advantages and limitations,
and they are both subject to the guidelines established by the Generic Access Profile
(GAP), which
Chapter 3
describes in detail.
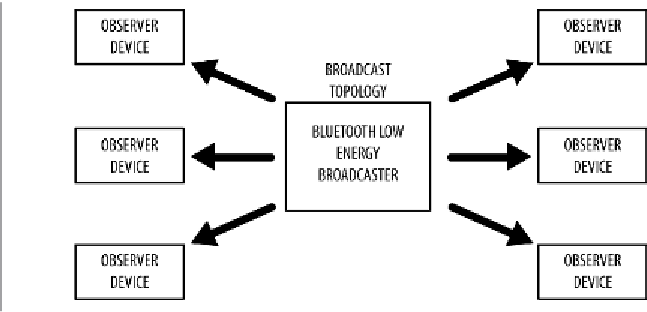
Broadcasting and Observing
Using connectionless
broadcasting
, you can send data out to any scanning device or
receiver in listening range. As illustrated in
Figure 1-3
, this mechanism essentially allows
you to send data out
one-way
to anyone or anything that is capable of picking up the
transmitted data.
Figure 1-3. Broadcast topology
Broadcasting defines two separate roles:
Broacaster
Sends nonconnectable
advertising
packets periodically to anyone willing to receive
them.
Observer
Repeatedly scans the preset frequencies to receive any nonconnectable advertising
packets currently being broadcasted.
Broadcasting is important to understand, because it's the only way for a device to trans‐
mit data to more than one peer at time. You broadcast data out by taking advantage of
the the advertising features of BLE, as discussed in more detail in
“Advertising and
Scanning” on page 19
and
“Broadcast and Observation” on page 38
.