Geology Reference
In-Depth Information
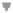
Time-shifted
zero-phase
wavelet
Decomposed into single
frequency components
Plot of phase
against frequency
Phase
0
Time zero
Time shift
-180
-360
Frequency
Time
Time
Figure 3.4
Linear phase wavelet; illustrating that this phase behaviour is effectively associated with a time shift (J. Chamberlain, personal
communication)
a)
b)
Source Signature
18db/oct low-cut
18+24 db/oct low-cut
0
0
50
50
100
100
Frequency
150
150
Reflection
Refraction
Transmission
Attenuation
Earth Filter
10
0
a: blue
b: red
10
-1
10
-2
Amplitude spectra
0
50
100
Frequency Hz
Figure 3.6
Two minimum phase wavelets with similar bandwidth
Note the marked differences in wavelet shape.
Frequency
tie is lower in frequency and roughly symmetrical with a
phase of around 180°.
These effects are controlled by attenuation, which
varies with the lithology and state of consolidation.
Seismic Trace
Figure 3.5
Seismic bandwidth and the Earth filter.
26