Geology Reference
In-Depth Information
Rock physics for seismic modelling
Chapter
8
8.1 Introduction
Seismic amplitudes are interpreted using models gen-
erated from well data and supported by a range of
knowledge collectively described as
anisotropic effects may also be required. Conditioned
logs are the basis for well ties (
Chapter 4
).
Rock characterisation (introduced in
Chapter 5
)
aims to describe seismic litho-facies and analyse the
relationships between rock and acoustic properties.
Mineralogy, porosity, pore types, fluid type and
effective pressure are all factors to be evaluated from
the log data (e.g. Castagna,
1993
). In addition, any
preferred vertical ordering of lithologies should be
established as this information can be used in gener-
ation of various geological scenarios. The presence of
distinct depth or sedimentological trends may in cer-
tain situations enable predictions outside the meas-
ured range (Avseth et al.,
2003
).
As described in
Chapters 2
and
5
, seismic models
can take various forms, such as single interface AVO
models, 1D angle synthetics, and various 2D models
.
This chapter describes the practical rock physics rele-
vant for the interpreter to begin constructing suitable
models for interpreting seismic signatures. The key
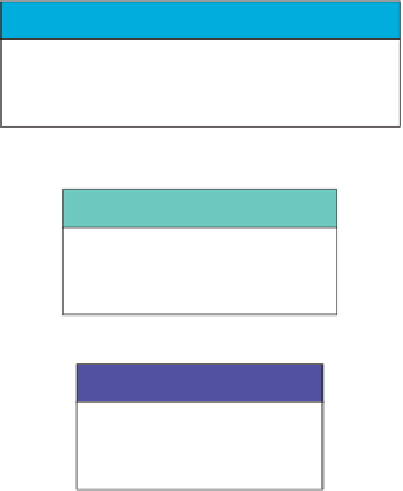
objectives in this use of rock physics (
Fig. 8.1
) are:
(1) log preparation and conditioning,
(2) rock characterisation from logs,
(3) seismic modelling.
'
rock physics
'
Conditioning of log data involves editing log curves
and making predictions for erroneous or missing
sections as well as making corrections for the adverse
effects of drilling mud on log measurements (i.e. cor-
recting for invasion). In deviated holes, corrections for
PETROPHYSICAL LOG QC AND ANALYSIS
Environmental and borehole corrections
Depth shifts
Mineral fractions, water saturation, porosity
LOG CONDITIONING
ROCK CHARACTERISATION
SEISMIC MODELLING
Log edits
Invasion corrections
Fluid substitution
Defining seismic lithofacies
Log upscaling
Statistics
Well ties, Avo plots, 1D/2D synthetics
Model crossplot templates
Pseudo-well data
ROCK PHYSICS MODELS
Empirical and physically
based models
150
Figure 8.1
Rock physics analysis of log data.