Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
between fields in South America and concentrated animal feeding operations in Asia
(Wald
et al
., this volume).
This third phase has greatly expanded the global supply of meat and calories and,
for reasons of environmental degradation and wealthy consumer demand described
below, made it harder for many population groups to access affordable grains and
pulses. Not only has the relative proportion of available foods hanged over the mil-
lennia, so too has the content of foods. Some of these later hanges have been rapid.
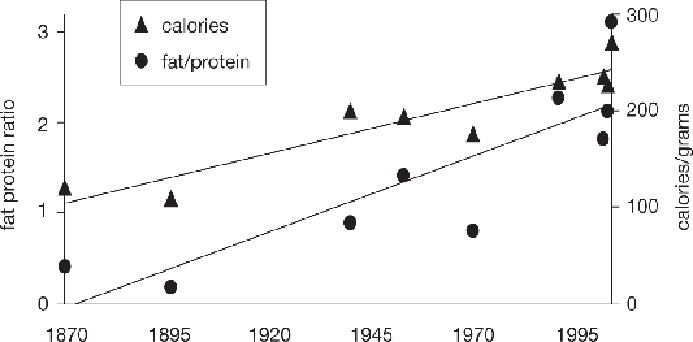
For example, the fat content in intensively farmed animals whose exercise capacity
is extremely restricted is muh higher than the 'extensively farmed' animals from
fifty years ago; and higher still than in wild animals, even at their time of peak fat
storage at the start of winter (Cordain
et al.
, 2005). his is documented for hikens
ratio of essential faty acids has also hanged (Wang
et al.
, 2010), almost certainly in
adverse ways.
Figure 7.1 he percentage of fat found in hikens, now mostly reared in industrial conditions,
has risen substantially.
Source: adapted from Wang (2010)
Given this context, knowledge of what we can reasonably expect of food yields
and of the nutritional quality of foods and their destinations is of great importance.
Using WHO Expert Commitee 'healthy diet and population nutrient intake goals',
Hawkesworth
et al.
, (2010) assess the performance of the global agricultural system