Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
Travelling waves
1
3
1′
.
N
S
Standing waves
2
2′
3
.
Global cavity mode
2′
2
.
Equator
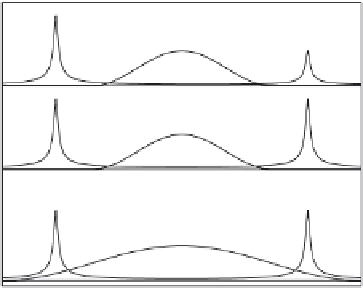
Fig. 3.2.
A sketch of spatial amplitude distributions on the ground caused by various
resonances. Index 1 refers to the high-frequency resonance on traveling waves. Indices
2and2
mark resonances on standing Alfven waves. 3 refers to an FMS-wave that
has reached the ground directly
i.e. intensified suppression of all types of oscillation except the basic one, can
occur due to variable properties of the magnetosphere tail boundary.
Continuous oscillations should occur in the open magnetosphere when
there is a strong reflection of the waveguide modes moving from the dayside
magnetosphere to its tail and reflected from its 'open' ends. Such an effect is
observed in acoustics during resonance oscillations of open tubes, whistles, etc.
If, for instance, the magnetosphere tail is regarded as a cylindrical waveguide,
then, according to McKenzie (1970), the plasma sheet can oscillate with a
period of 6 min.
Figure 3.2 demonstrates a stylized picture of the latitudinal dependencies
for various resonances:
1. resonance on travelling waves;
2. resonance on standing waves;
3. global cavity mode.
Index 1 in Fig. 3.2 marks the high-frequency resonance on traveling waves.
This resonance intensification can be observed at high latitudes. The differ-
ence in the magnitudes of intensity maxima at conjugate points 1 and 1
is connected with the choice of the preferential northern propagation for an
FMS-wave. Indices 2 and 2
mark resonances on standing Alfven waves. The
highest cavity mode harmonics excite corresponding FLR-harmonics. 3 refers
to an FMS-wave that has reached the ground directly. Oscillations of the
same frequency could in this case be recorded as wide apart in the latitude
and longitude observation points. The amplitude decreases to middle and low
latitudes is concerned with FMS-wave attenuation as it penetrates into the
magnetosphere and with non-resonance excitation of Alfven waves.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search