Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
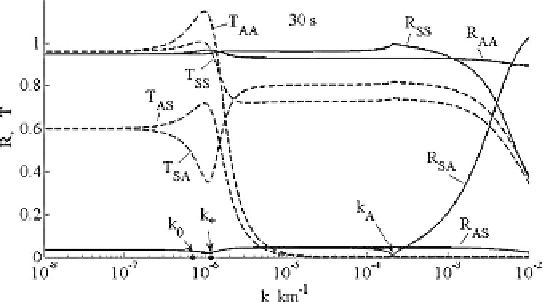
Fig. 7.6.
Dependencies of the reflection
R
and transmission
T
matrices on the
horizontal wavenumber
k
for the dayside ionosphere. The second subindex refers
to the incident wave (
A
=Alfven wave,
S
= FMS-wave), the first one refers to
a converted wave. For instance,
R
SA
is reflection coecient of the incident Alfven
wave into the reflected FMS-wave. The wave period
T
= 30 s, and other parameters
are given in Table 7.3
Meridional Propagation
Figure 7.6 demonstrates various elements of
R
and
T
matrices depending on
horizontal wavenumber
k
=
k
x
for pulsations with periods
T
=30s.The
curves for other longer periods
T
are not shown but are very similar to those
of Fig. 7.6. The parameters for this example are indicated in Table 7.3. The
ground is a half-space (
H
=
10
3
,and
Y
=
∞
),
X
=4
πΣ
P
/c
=4
.
86
×
10
3
.
The first thing to pay attention to is the steep decrease of
T
AS
and
T
AA
at
k
4
πΣ
H
/c
=5
.
7
×
k
∗
. It means that a considerable contribution to the ground field in
the electric mode will be made only by spatial harmonics with
k
k
∗
:
const
,
at
k
∗
<k<h
−
1
T
SA
≈
const
,
T
SS
≈
and damp exponentially at
k>h
−
1
.
Comparison of the approximation formula (7.129) for
R
AA
(
k
)andnumer-
ical results presented in Fig. 7.6 shows that (7.129) is indeed valid in a wide
range of horizontal wavenumbers (
k>k
∗
). Minor differences between calcu-
lated values and those computed by (7.129) correspond to correction terms
discarded in (7.129).
Dependencies of the vertical magnetic ground component
b
z
(
k
)fordiffer-
ent periods are shown in Fig. 7.7. Panel (a) is the amplitude of
b
z
,
(b) is its
phase. The curves 1
,
2
,
3
,
4 correspond to 30
,
100
,
300
,
and 1000 s respectively.
One can see that there is a maximum in the spatial spectrum shifting with
the oscillation period.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search