Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
Im
k
Imκ
g
=0
Im
κ
S
=0
k
3
=−
k
0
ε
g
1/2
k
2
=−
k
0
ε
m
1/2
k
1
=−
k
0
ε
m
1/2
Re
k
k
4
=−
k
0
ε
g
1/2
Imκ
s
=0
Im
κ
g
=0
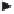
Fig. 7.3.
Lo
ca
tion of cuts Im
κ
g
=Im
κ
s
= 0 and branch points
k
1
,
2
=
±k
0
√
ε
m
,
k
3
,
4
=
±k
0
√
ε
g
on the complex plane of wave numbers
k
In the case of the finite conductivity layer underlain by a perfect conductor,
only two sheets remain:
•
the physical sheet: Im
κ
s
>
0and
•
the non-physical sheet: Im
κ
s
<
0.
Apart from branch points, the poles of
R
and
T
can appear on the
complex plane, and their location is determined by the roots of
∆
(
k
) (7.101):
∆
(
k
)=0
.
(7.106)
The Role of a Magnetic Inclination
Before proceeding to the investigation of
R
(
k
)and
T
(
k
) in various wavenum-
ber ranges, note that the character of the reflection of MHD-waves does not
Table 7.2.
Numeration of the sheets of the Riemann surface
Physical sheet
Non-physical sheets
1. Im
κ
g
>
0andIm
κ
s
>
0
2. Im
κ
s
<
0, Im
κ
g
>
0
3. Im
κ
s
<
0, Im
κ
g
<
0
4. Im
κ
s
>
0, Im
κ
g
<
0










Search WWH ::

Custom Search