Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
B
0
(
a
)
(
b
)
y
ρ
B
0
x
ϕ
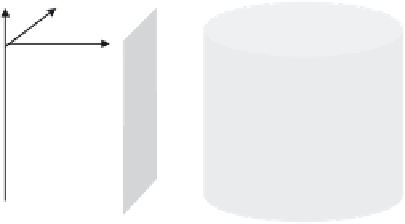
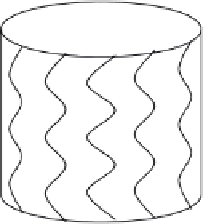
Fig. 4.1.
Sketches of the magnetic field-lines disturbed by (
a
) linearly polarized
shear Alfven wave and (
b
) by a torsional shear Alfven wave
Arbitrary initial perturbation is carried along the field-lines at Alfven ve-
locity with constant shape and without spreading in the transverse direction.
Guiding by field-lines is probably the most important property of Alfven waves
which is unchanged in inhomogeneous plasmas and even under finite curvature
of field-lines.
An arbitrary Alfven perturbation in homogeneous plasma can be presented
as a superposition of disturbances of non-interacting field-lines. For a field line
with coordinates (
x
0
,y
0
) displacement can be written as
ξ
+
(
x, y
)=
∇
×
δ
(
x
−
x
0
,y
−
y
0
)
z
,
where
δ
(
x, y
) is the Dirac delta-function. However, in an inhomogeneous
plasma, interaction arises between perturbations propagating along adjacent
field-lines and a bundle of interacting field-lines is excited as a result. Guiding
along field-lines is conserved in this case, as well.
Magnetosonic Waves
Consider two other types of waves with vortex
Ω
and longitudinal current
j
vanish. The longitudinal magnetic field
b
, transversal compression
ξ
⊥
and longitudinal displacement
ξ
are non-zero. It is convenient to use the
perturbation of the longitudinal magnetic field and longitudinal displacement
in the description of these waves. Applying transverse operator
∇
·
∇
⊥
·
to (4.24)
and (4.25), we obtain for
b
and
ξ
:
b
B
0
b
B
0
−
,
∂
2
∂t
2
∂ξ
∂z
1
c
2
A
2
2
⊥
∇
−
=
−
β
∇
(4.33)
∂
2
∂z
2
−
ξ
||
=
∂
2
∂t
2
1
c
s
∂
∂z
b
B
0
.
(4.34)












Search WWH ::

Custom Search