Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
As
Vs
Ap
Vp
Ap
Vs
Ap
Vp
EKG
ARP
AVI
ABVP
PVARP
TARP
VRP
AEI
PAVB
ABAS
ABAP
PVAB
VBVS
VBVP
PAVB
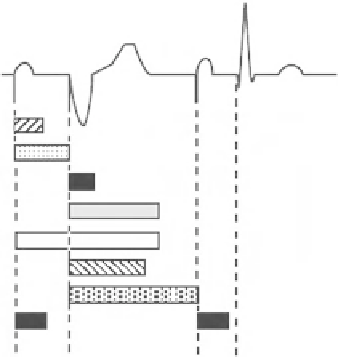
Fig. 9.7
DDD blanking periods
Fig. 9.8
DDD refractory periods
•
Ventricular blanking after ventricular sensing. Throughout
this period, ventricular sensing after a sensed ventricular
event is deactivated.
Ventricular blanking after ventricular pacing. Throughout
Certain manufacturers' systems are equipped with a
sophisticated PVAB system to eliminate far-field R waves
sensed in the atrium [20]. Atrial events sensed during PVAB
are used to measure tachycardia.
•
this period, ventricular sensing after a paced ventricular
event is deactivated.
All the blanking periods listed above must be made avail-
able by all manufacturers and in all types of devices [20, 63].
In dual-chamber modes, atrial pacing also triggers postatrial
ventricular blanking (PAVB) in the ventricular channel. This
period avoids the inhibition of the ventricular channel and
subsequent asystole because of sensing of an atrial event in
right ventricle. If the PAVB is too short, crosstalk may occur,
which may be sensed by the ventricular channel. On the
other hand, if the PAVB is too long, the pacemaker may not
sense premature ventricular action (e.g., ventricular extra-
systoles), which may lead to ventricular pacing during intrin-
sic ventricular action.
The length of a noise rejection period is in the order of
tens of milliseconds, and it is made available in certain forms
by all manufacturers. Sometimes it may be programmable.
Any time a signal is detected during a noise detection period,
the period is restarted at the moment the signal was detected.
Ventricular pacing triggers the noise rejection period and
atrial blanking period (postventricular atrial blanking
[PVAB]) in the atrial channel. It may be programmable. The
aim is to set the length of blanking so that far-field R wave
sensing in the atrium is prevented and, simultaneously, the
possibility of sensing spontaneous atrial activity is main-
tained. The length of blanking in the other chamber after a
pacing pulse may differ for unipolar and bipolar sensing
configurations or depending on the pacing pulse amplitude -
it is usually longer for a unipolar configuration and higher
amplitude. Some systems distinguish atrial blanking during
ventricular pacing and atrial blanking during ventricular
sensing. VA interval measurement can be used to check the
far-field R wave sensing.
9.4
Refractory Periods
Refractory periods are phases after a paced or sensed event
when input amplifiers of the sensed signal are already acti-
vated and the device senses possible intrinsic cardiac activity
(Fig.
9.8
). The pacemaker timing is not, however, affected by
this sensed activity. During the refractory period, a sensed
event cannot trigger a particular timing interval in a particu-
lar channel. Each refractory period starts with a blanking
period, during which no sensing is performed. Like the
blanking periods, the purpose of refractory periods is also to
exclude triggering or inhibiting the pacemakers' operation
based on the detection of inappropriate signals, such as retro-
grade P waves, far-field R waves, or noise. Possible sensed
events are classified as refractory, and the response to these
events is adapted to this. The programmability of refractory
periods depends on the selected pacing mode and on the
manufacturer.
In single-chamber atrial modes (AAT, AAI[R]), the atrial
refractory period (ARP) is defined as an interval after an
atrial event, be it paced or sensed, in which sensed atrial
activity does not inhibit or trigger an atrial pacing pulse.
A postventricular ARP (PVARP) is defined only in dual-
chamber pacing modes (with the exception of D00). The
PVARP follows a paced, sensed, or refractory sensed ven-
tricular event, and an atrial event during this period is then
classified as refractory. Hence, it does not inhibit atrial pac-
ing or trigger an AVI after a sensed event. The PVARP avoids
the inhibition of atrial pacing caused by sensed far -R waves,