Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Fig. 4.2
Sinus arrhythmia [ 24 ] (Used with permission of C. Cihalik, Palacky University Olomouc, Czech Republic )
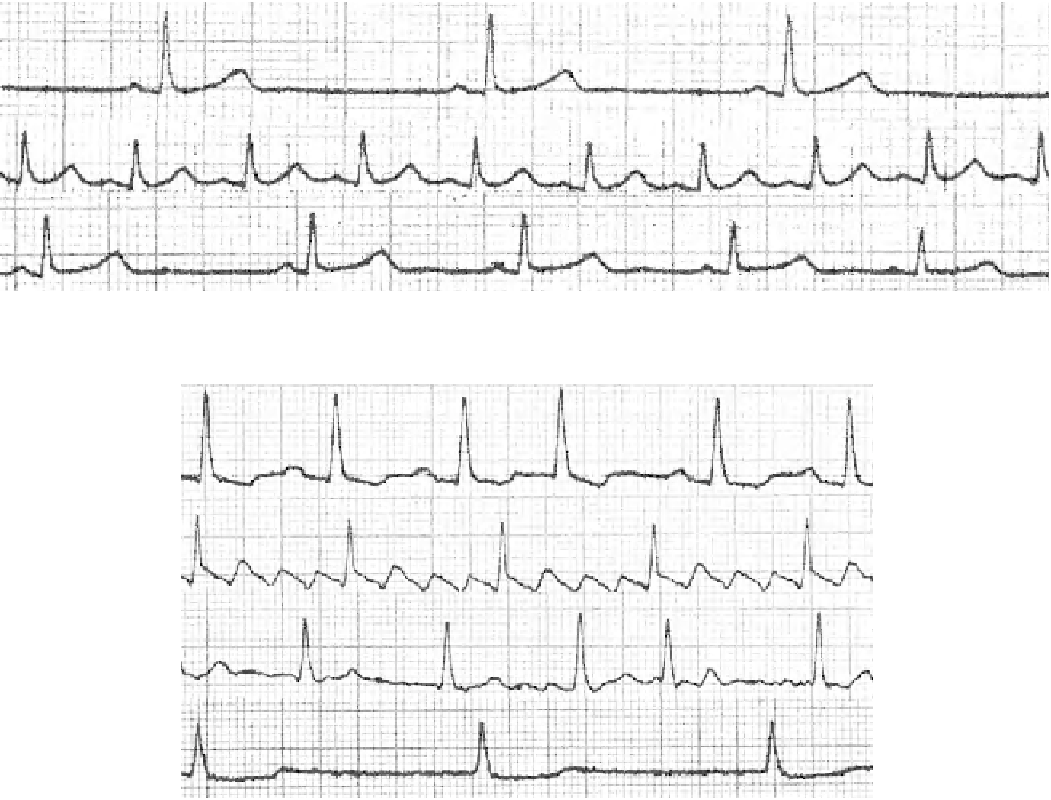
Fig. 4.3
Supraventricular arrhythmia [24] (Used with permission of C. Cihalik Palacky University Olomouc, Czech Republic)
4.1.2
Supraventricular Arrhythmias
4.1.2.2 Atrial Tachycardia
Atrial tachycardia originates from a focus anywhere in the
atria except the sinus node. The most commonly involved
mechanism is abnormal automaticity; less frequently, reen-
try is the mechanism. The heart rate may be more than 200
beats/min. The shape of the P wave depends on the distance
from the sinus node. The condition is treated with antiar-
rhythmic agents.
Supraventricular arrhythmias (Fig.
4.3
) originate and persist
in the region of the atria, the sinoatrial and AV nodes, and
accessory AV pathways [ 25 ] .
4.1.2.1 Supraventricular Extrasystoles
Supraventricular extrasystoles are premature contractions
originating from anywhere except the sinus node. Based on
the source of pathological activity, extrasystoles can be
divided into atrial, junctional, and ventricular. In supraven-
tricular extrasystoles, the shape of the P wave depends on the
distance from the sinus node. A supraventricular extrasystole
(premature atrial contraction) is followed by an incomplete
compensatory pause because the atrial impulse is usually
conducted in a retrograde fashion to the sinus node and dis-
charges the impulse being generated in it. A new impulse is
then generated from the beginning and is further conducted
in a normal interval.
4.1.2.3 Atrioventricular Nodal Reentrant
Tachycardia
AV nodal reentrant tachycardia (AVNRT) is the most fre-
quent regular paroxysmal tachycardia originating from the
atrial part of the AV node. It is based on a reentry mechanism
and has a sudden onset and end. The most common form has
a slow conduction from the atrium to the ventricle and a
rapid conduction back. Atrial and ventricular activation
occur simultaneously and, on a surface ECG, the P waves
are hidden in the QRS complex or follow it immediately.