Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
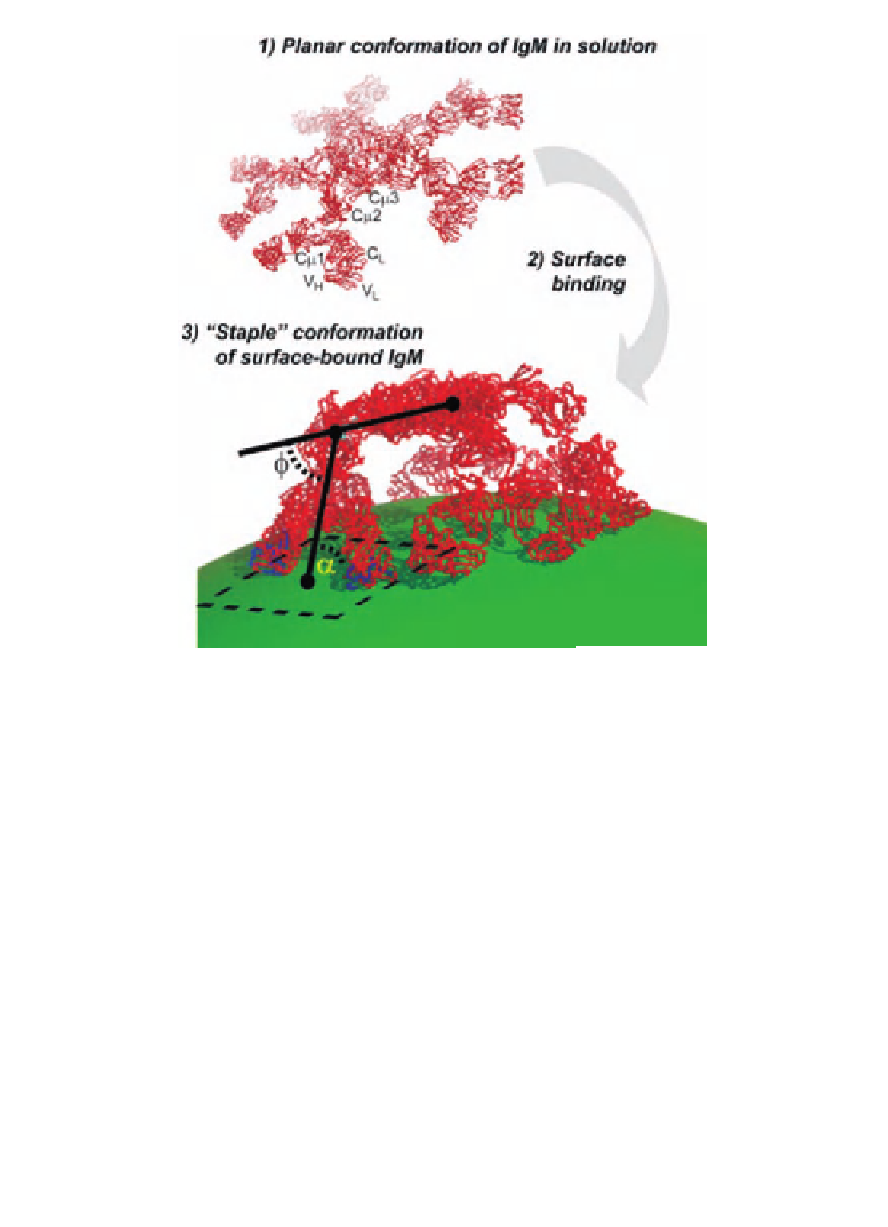
Figure 10.1
Three-step model for the binding of IgM to target surfaces. In
solution IgM is a planar structure of five structural units each containing four
constant (C
µ
1-4) domains and one variable (V
) domain in the heavy chain
H
) domain in the light chain. In 1)
the planar structure described by Perkins et al. [4] is shown with indications
of the approximate position of some of the structural domains. The dynamics
of binding of IgM to target surfaces (2) is not well understood, but suggestions
were [71] made that the process brings IgM into the “staple” conformation,
which permits binding of the C1 complex and hence initiates complement
activation. Perkins et al. suggested that the specific requirement would be
that the angle
and one constant (C
) and one variable (V
L
L
. Pedersen et al. recently suggested that
IgM binding to curved surfaces would regulate
f
takes a value of 60
°
according to the curvature
by assuming that the contact between epitopes and the variable domains in
IgM is geometrically well defined with a characteristic angle
a
f
[70]. In (3),
IgM is shown drawn to scale and bound to a sphere with a diameter of 66
nm (modified from [70]). The artwork was kindly made by Dr. T. Boesen,
Aarhus University.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search